PIB ANALYSIS FOR UPSC CIVIL SERVICES EXAM
TOPICS COVERED
- Prime Minister – Science, Technology and Innovation Advisory Council, Principal Scientific Adviser
- INDRA 2018
- LEAP and ARPIT
- Hunaar Haat
- Toll operate Transfer
- Tropical Cyclones
1 . Prime Minister -Science, Technology and Innovation Advisory Council
Prime Minister interacts with the members of his Science, Technology and Innovation Advisory Council (PM-STIAC)
About Principal Scientific Adviser
The Office of the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India (PSA’s Office) was set-up in November, 1999 by the Cabinet Secretariat, primarily, to:
- Evolve polices, strategies and missions for the generation of innovations and support systems for multiple applications,
- Generate science and technology tasks in critical infrastructure, economic and social sectors in partnership with Government departments, institutions and industry, and
- Function as the Secretariat to the Scientific Advisory Committee to the Cabinet, with the Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India as its Chairman.
About Prime Minister -Science, Technology and Innovation Advisory Council
- The PM-STIAC is an overarching Council that facilitates the PSA’s Office to assess the status in specific science and technology domains, comprehend challenges in hand, formulate specific interventions, develop a futuristic roadmap and advise the Prime Minister accordingly.
- PSA’s Office also oversees the implementation of such interventions by concerned S&T Departments and Agencies and other government Ministries.
- The other important terms of reference of the Council is to formulate, converge, collaborate, co-ordinate and implement multi-stakeholder policy initiatives, mechanisms, reforms and programmes aimed at:
- Synergizing S&T covering fundamental to applied research in collaboration with multiple stake holders both in central and state governments
- Enabling future preparedness in emerging domains of science and technology
- Formulating and coordinating major inter-ministerial S&T missions
- Providing an enabling ecosystem for technology led innovations and techno-entrepreneurship
- Driving innovation and technology delivery towards solving socio-economic challenges for sustainable growth
- Fostering effective public-private linkages for driving research and innovation
- Developing innovation clusters with multiple stakeholders including academia, industry and government
- Skilling in current and futuristic technologies.
2 . EXERCISE INDRA- 2018
Curtain Raiser: INDO-Russian joint exercise INDRA 2018
- EXERCISE INDRA 2018 is the joint military exercise between Indian and Russia on combating insurgency under the aegis of United Nations (UN)
- It will be conducted at Babina Field Firing Ranges, Babina Military Station from 18 November 2018.
- Company sized contingents of the 5th Army of the Russian Federation and a Mechanised Infantry Battalion of Republic of India will participate in the training exercise spanning for eleven days including induction and de-induction of the Russian contingent
- The tenth exercise in the series of Exercise INDRA is aimed at sending a strong message to the world with an intent of appreciation of interoperability between Indian and Russian Armies for joint tactical level operations in the peace keeping / enforcement environment under the aegis of UN.
3 . LEAP and ARPIT
Leadership for Academicians Programme (LEAP)
- Leadership for Academicians Programme is a three weeks Flagship leadership development training programme (2 weeks domestic and one week foreign training) for second level academic functionaries in public funded higher education institutions.
- The main objective is to prepare second tier academic heads who are potentially likely to assume leadership roles in the future.
- The programme would provide senior faculty, with high academic credentials, the required leadership and managerial skills including skills of problem-solving, handling stress, team building work, conflict management, developing communication skills, understanding and coping with the complexity and challenges of governance in HEIs, financial & general administration.
- The implementation of LEAP Programme will be through 15 NIRF top ranked Indian Institutions
- The foreign Universities identified for the training are also within the top 100 in the world global rankings.
Annual Refresher Programme in Teaching (ARPIT)
- Annual Refresher Programme in Teaching (ARPIT), a major and unique initiative of online professional development of 15 lakh higher education faculty using the MOOCs platform SWAYAM.
- For implementing ARPIT, 75 discipline-specific institutions have been identified and notified as National Resource Centres (NRCs) in the first phase, which are tasked to prepare online training material with focus on latest developments in the discipline, new & emerging trends, pedagogical improvements and methodologies for transacting revised curriculum.
4 . Hunaar Haat
- Hunar Haat is organised by the Minority Affairs Ministry to provide an opportunity, as well as domestic and international exposure to the master artisans from across the country.
5 . Toll Operate Transfer Project
- Under the TOT model, successful bidders are required to pay the amount upfront.
- The NHAI uses the upfront receivables exclusively for funding construction of highways.
- Bidders will recoup their investments and returns by collecting toll over the lease tenure.
- Operation and Maintenance (O&M) obligation of such projects shall be with the Bidders till the completion of the lease period.
- Projects to be undertaken in the TOT model are to be treated as Public-private-partnership (PPP) projects.
6 . Tropical Cyclones
Cyclonic storm ‘GAJA’ over West central and adjoining East central & South Bay of Bengal: Cyclone Alert for Tamil Nadu & Puducherry coast: Yellow Message
About Tropical Cyclones
- A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center, a closed low-level circulation, and a spiral arrangement of numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rainfall.
- Tropical cyclones are like giant engines that use warm, moist air as fuel. That is why they form only over warm ocean waters near the equator.
- The warm, moist air over the ocean rises upward from near the surface. Because this air moves up and away from the surface, there is less air left near the surface ie. the warm air rises, causing an area of lower air pressure below.
- Air from surrounding areas with higher air pressure pushes in to the low pressure area.
- Then that “new” air becomes warm and moist and rises, too. As the warm air continues to rise, the surrounding air swirls in to take its place.
- As the warmed, moist air rises and cools off, the water in the air forms clouds.
- The whole system of clouds and wind spins and grows, fed by the ocean’s heat and water evaporating from the surface.
- Storms that form north of the equator spin counterclockwise. Storms south of the equator spin clockwise. This difference is because of Earth’s rotation on its axis.
- As the storm system rotates faster and faster, an eye forms in the center. It is very calm and clear in the eye, with very low air pressure. Higher pressure air from above flows down into the eye.
- When the winds in the rotating storm reach 39 mph, the storm is called a “tropical storm.” And when the wind speeds reach 74 mph, the storm is officially a “tropical cyclone,” or hurricane.
- Tropical cyclones usually weaken when they hit land, because they are no longer being “fed” by the energy from the warm ocean waters. However, they often move far inland, dumping many inches of rain and causing lots of wind damage before they die out completely.
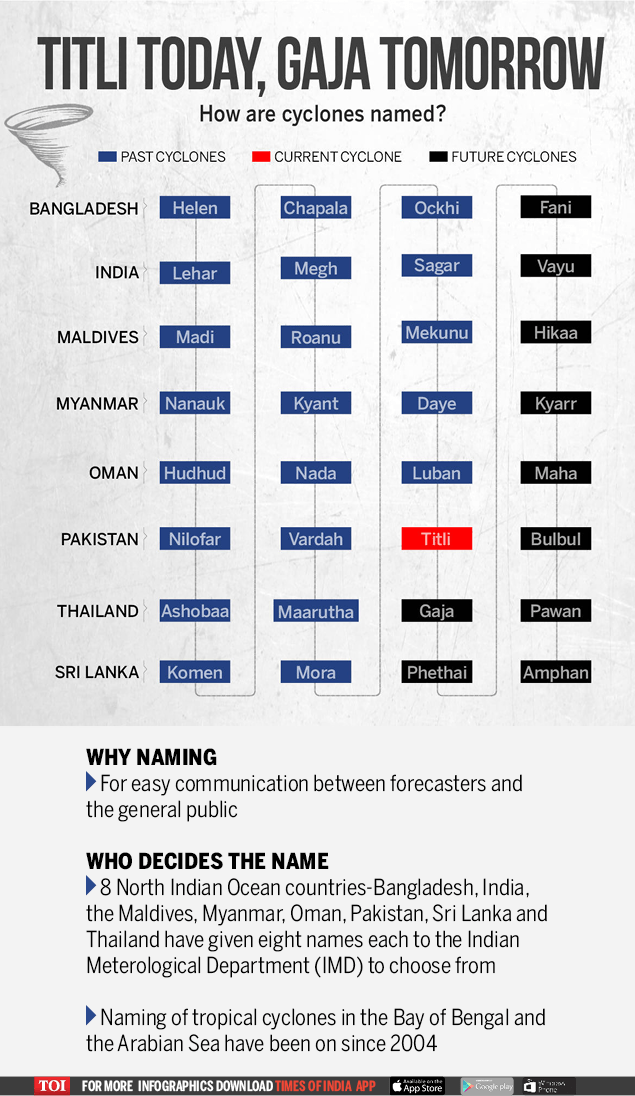
How Cyclones are named in South Asia
- Countries in the South Asian region given below submits 10 different names which can be given to a cyclone
- Out of 10 different names 8 names are selected by Regional specialised meteorological centre.
- They prepare 8 different list with one name submitted by one country ie. total 8 names submitted by 8 countries
- As and when cyclone occurs one name as per the order is selected and assigned to the cyclone
This is very useful information for the aspirants.thank you for this