PIB Analysis for UPSC CSE
Topics Covered
- National corporate social responsibility awards
- 15 point charter reform
- Paramahansa Yogananda
- Green Channel filing
- Lymphatic Filariasis
- International Solar Alliance
- Pradhan Mantri Van Dhan Yojana (PMVDY)
- Gottiprolu
- GB Pant Institute of Himalayan Environment & Development
- Intensified Mission Indradhanush (IMI)
- Facts for Prelims :Future Investment Initiative, e-office
1 . National Corporate Social Responsibility Award
Context : The President of India, Shri Ram Nath Kovind, presented the National Corporate Social Responsibility Awards
About the Awards
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India has instituted National Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Awards to recognize companies that have made a positive impact on the society through their innovative & sustainable CSR initiatives.
The National CSR Awards seek to:
- Recognize the companies that have positively impacted both business and society by taking a strategic approach to CSR through collaborative program.
- Recognize the companies that are leading transformation by integrating sustainability in their core business model.
- Recognize companies for implementing measures for conservation and sustainable management of the biodiversity and ecosystem in the value chain.
- Identifying innovative approaches and employing application and technologies that will help to build a robust CSR programs to further the cause of inclusive and sustainable development.
Categories of Awards
- The Ministry of Corporate Affairs has instituted National CSR Award (NCSRA) to recognize corporate social responsibility (CSR) for inclusive growth and sustainable development. This Award seeks to recognize the companies that have made a transformative impact on society.
- The NCSRA seeks to recognize outstanding projects in following three categories:
- Four awards for excellence in CSR, based on CSR spend
- Five awards for CSR projects in Aspirational Districts
- Eleven awards for CSR projects in National Priority Areas.
- Three separate awards are for micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs).
2 . 15 point charter reform
Context : Vice President seeks a new political normal based on 15 point reform charter for better functioning of Parliament
15 Point Reform Charter for Better Functioning of Parliament
- Political Conscience: New political consciousness amongst legislators to review their roles and responsibilities.
- Quorum: Political parties must ensure attendance of at least 50% of their legislators throughout the proceedings of the Houses by adopting a roster system.
- This was needed in the backdrop of required Quorum (of 10% of the strength of the Houses), which if not met, leads to the adjournment of the House.
- Whip: Review of Whip system which hinders the freedom of expression of the legislators.
- This will allow a reasonable degree of dissent without impacting the stability of the government.
- Anti- Defection: Review of the Anti Defection Law to rectify the areas like incentivizing legislators to resort to actions that invite expulsion from the party besides providing for time-bound disposal of defection cases by the Presiding Officer.
- Department Related Standing Committees: Measures for effective functioning of Department Related Standing Committees like longer tenure (instead of the present one year), promoting specialization, etc were needed.
- Legislative Impact Assessment: A detailed framework for pre and post Legislative Impact Assessment was needed.
- Every legislative proposal must incorporate a detailed account of social, economic, environmental and administrative impact for wider awareness and subsequent legal assessment.
- Voting Preferences: Need for moving away from identity-based voting to that of development-oriented exercise of voting preferences. Role of caste, community, region, and religion in influencing the voting preferences needs to be minimized.
- Responsible Government and Opposition: Need for responsive governments positively acting on the concerns of the opposition and the need for responsible and constructive opposition while resorting to available parliamentary instruments.
- Simultaneous Polls: Building consensus on the proposal of simultaneous polls to allow unrestricted governance.
- Reservation of Women: Enacting for reservation of women in legislatures.
- Rules and Regulations: Making rules that automatically take action against erring members in case of interruptions and disruptions. Need for timely and effective action against legislators for non-ethical conduct.
- Transparency & Accountability: Regular publication of reports by the Secretariats of Legislatures on the attendance of Members and their participation in debates.
- Addressing the concern of a rising number of legislators with criminal records.
- Setting up of special courts for time-bound adjudication of criminal complaints against legislators.
- A minimum number of sittings for both the Houses of Parliament and State Legislatures per year need to be appropriately prescribed.
3. Paramahansa Yogananda
Context : The Union Minister for Finance & Corporate Affairs Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman released a special commemorative coin on Paramahansa Yogananda to mark his 125th birth anniversary here today .
About Paramahansa Yogananda
- Paramahansa Yogananda was an Indian monk, yogi and guru who introduced millions to the teachings of meditation and Kriya Yoga through his organization Self-Realization Fellowship (SRF) / Yogoda Satsanga Society (YSS) of India.
- A chief disciple of the Bengali yoga guru Swami Sri Yukteswar Giri, he was sent by his lineage to spread the teachings of yoga to the West, to prove the unity between Eastern and Western religions and to preach a balance between Western material growth and Indian spirituality
- His long-standing influence in the American yoga movement, and especially the yoga culture of Los Angeles, led him to be considered by yoga experts as the “Father of Yoga in the West
- He published his book Autobiography of a Yogi in 1946
About Kriya Yoga
- Kriya Yoga is an ancient meditation technique of energy and breath control, or pranayama. It is part of a comprehensive spiritual path, which includes additional meditation practices along with right living.
- Yogananda then popularized Kriya Yoga through his book, Autobiography of a Yogi, and through his public teaching in the West. Kriya has been taught in an unbroken link of spiritual succession to this day.
4 . Green Channel Filing
Context : CCI receives combination notice under green channel scheme,
Background
- As part of its ongoing and regular efforts to make M&A filings approval faster, the CCI has introduced an automatic system of approval for combinations under Green Channel.
- Under this process, the combination is deemed to have been approved upon filing the notice in the prescribed format. This system would significantly reduce time and cost of transactions.
What is the ‘Green Channel’?
Green Channel approvals can be availed in combinations where:
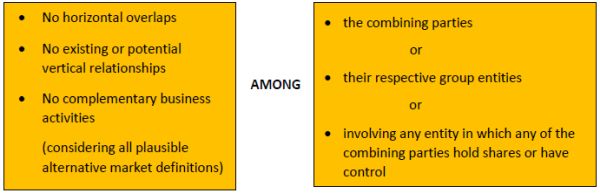
The amended Combination Regulations do not provide any threshold for the percentage of shares. In other words, at least – theoretically – even a single share could render the combination illegible under the Green Channel.
5 . Lymphatic Filariasis
About Lymphatic filariasis
- Lymphatic filariasis, considered globally as a neglected tropical disease (NTD), is a parasitic disease caused by microscopic, thread-like worms.
- The adult worms only live in the human lymph system. The lymph system maintains the body’s fluid balance and fights infections.
- Lymphatic filariasis is spread from person to person by mosquitoes.
- People with the disease can suffer from lymphedema and elephantiasis and in men, swelling of the scrotum, called hydrocele.
India’s effort
- Global Program to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis (GPELF) by the World Health Organization in 2000, endemic countries across the world including India have adopted a twin pillar strategy – prevention through Mass Drug Administration (MDA) using combination of 2 anti-filarial drugs (DEC and Albendazole), and, providing Morbidity Management and Disability Prevention (MMDP) services to those affected by the disease.
- Renewing India’s commitment towards elimination, the Government launched the Accelerated Plan for Elimination of Lymphatic Filariasis (APELF) in 2018, and as part of intensifying efforts towards elimination later rolled out Triple Drug Therapy (IDA) treatment in a phased manner.
- By the end of February 2019, India successfully rolled out IDA across 4 districts including Arwal in Bihar (20 December 2018), Simdega in Jharkhand (10 January 2019), Nagpur in Maharashtra (20 January 2019) and Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh (20 February 2019).
6 . International Solar Alliance
Context : The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy is hosting the second Assembly of International Solar Alliance (ISA)
About the Assembly
- The Assembly is the supreme decision making body of the ISA, and gives directions on various administrative, financial and programme related issues.
About International Solar Alliance
- The ISA, is an Indian initiative that was launchedby the Prime Minister of India and the President of France on 30 November 2015 at Paris, France on the side-lines of the COP-21, with 121 solar resource rich countries lying fully or partially between the tropic of Cancer and tropic of Capricorn as prospective members.
- The overarching objective of the ISA is to collectively address key common challenges to the scaling up of solar energy in ISA member countries.
- It also aims to undertake joint efforts required to reduce the cost of finance and the cost of technology, mobilize investments needed for massive deployment of solar energy, and pave the way for future technologies adapted to the needs.
- ISA has been positioned to help create the conditions that would make funding, developing and deploying solar applications on a large scale a reality. ISA is now perceived as key to achieving the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals and objectives of the Paris Agreement on Climate Change.
First Assembly of ISA
- The first Assembly of the ISA was attended by 78 countries, and they had affirmed their determination to accelerate the deployment of solar energy worldwide for achieving universal energy access at affordable rates.
- Recognizing that ISA has a major role in achieving Sustainable Development Goals, and objectives of the Paris Agreement on Climate Change, and that the ISA initiative would benefit the world at large, during the first Assembly of the ISA an Indian resolution to extend the Membership of the organisation to all countries that are Members of the United Nations was adopted.
Current Status
- As on date 81 countries of the 121 prospective member countries have signed the Framework Agreement of the ISA.
- Of these, 58 countries have ratified the same. The Assembly will be attended by the Ministers and delegates from member States, Observer States, ISA Partners, and other invitees.
Evaluation of ISA
- Since the first Assembly, ISA has initiated many activities and programmes.
- Demand for over 1000 MW solar power and 300000 solar water pumps has been aggregated from ISA member countries.
- Some of the major activities for building domestic capacity of the ISA member countries include ITEC Master Trainers Programme at NISE Gurugram; M. Tech programme for mid-career professionals at IIT, Delhi; STAR-C programme, and development of the INFOPEDIA.
- In order to understand the challenges and issues ‘on the ground’ and to strengthen support for ISA programmes, the ISA sent country missions to eight countries over the course of 2019 – to Benin, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Guinea, Malawi, Mali, Niger, Togo, and Uganda.
- ISA has significantly extended outreach and have partnered with over 40 organizations. These broadly include UN, Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs), Development Finance Institutions (DFIs), international and regional organizations and foundations, and private sector players.
Importance
Through this initiative, the countries, inter alia, share the collective ambition:
- To address obstacles that stand in the way of rapid and massive scale-up of solar energy;
- To undertake innovative and concerted efforts for reducing the cost of finance and cost of technology for immediate deployment of competitive solar generation; and
- To mobilise more than 1000 Billion US Dollars of investments by 2030.
- The Government of India has committed Rs.175 crore for setting up of ISA and till date released a sum of Rs 145 crore for creating a corpus fund, building infrastructure and meeting day to day recurring expenditure.
India’s contribution
- India has been providing all out support for realizing ISA’s vision and objectives.
- The Government of India has allotted 5 acres of land to the ISA in National Institute of Solar Energy (NISE) campus, Gurugram and has released a sum of Rs. 160 crore, i.e. US$ 26 million for creating a corpus fund, building infrastructure and meeting day to day recurring expenditure of the ISA up to the year 2012-22. As per commitment, India will release additional Rs. 15 crore, i.e. US$ 2.1 million in the year 2020-21.
- In addition, various Public Sector Enterprises of Government of India have contributed US$ 8 million for augmenting ISA corpus fund.
- Apart from these, India has set aside US$ 2 Billion for solar projects in Africa out of Government of India’s US$10 Billion concessional Line of Credit (LOC) for Africa.
- Exim Bank of India is implementing this line of credit in close coordination with ISA countries in Africa.
- On the side-lines of the 74th UN General Assembly, India announced allocation of US$ 12 million grant, and a concessional LOC of US$ 150 Million for Pacific Islands Developing States for undertaking solar, renewable energy and climate related projects.
7 . Pradhan Mantri Van Dhan Yojana (PMVDY)
The Van Dhan Scheme is an initiative of the Ministry of Tribal Affairs and TRIFED. It was launched on 14th April, 2018 and seeks to improve tribal incomes through value addition of tribal products.
The scheme will be implemented through Ministry of Tribal Affairs as Nodal Department at the Central Level and TRIFED as Nodal Agency at the National Level. At State level, the State Nodal Agency for MFPs and the District collectors are envisaged to play a pivot role in scheme implementation at grassroot level. Locally the Kendras are proposed to be managed by a Managing Committee (an SHG) consisting of representatives of Van Dhan SHGs in the cluster.
About PMVDY
- PMVDY is an initiative targeting livelihood generation for tribals by harnessing the wealth of forest i.e. Van Dhan.
- The programme aims to tap into traditional knowledge & skill sets of tribals by adding technology & IT to upgrade it at each stage and to convert the tribal wisdom into a viable economic activity. The initiative shall provide enhanced livelihood to about 45 lakhs tribal gatherers in one year.
- The Van Dhan initiative shall promote and leverage the collective strength of tribals to achieve a viable scale to take on the predatory market forces in the areas where these are still prevalent.
- Proposition is to set-up tribal community owned Minor Forest Produce (MFP)-centric multi-purpose Van Dhan Vikas Kendras (the Kendra) in predominantly tribal districts.
- About 6000 Van Dhan Kendras are proposed to be set up in span of 2 years i.e. 3000 Kendras to be set-up in each year, which will be further continued based on evaluation of their performance and also expanded every year.
8 . Gottiprolu Excavation
Context : The 1st phase of excavation by a team of Archaeological Survey of India’s Excavation Branch – VI, Bangalore at Gottiprolu near Naidupeta in Nellore (now renamed as Sri Potti Sri Ramulu) district, Andhra Pradesh has discovered the remains of a huge settlement surrounded by a massive brick enclosure.
Details of the excavation
- The site of Gottiprolu lies on the right bank of a distributary of river Swarnamukhi about seventeen kilometers east of Naidupet and eighty kilometers from Tirupati and Nellore.
- The proximity of the site to the seacoast suggests that the site could have served as a strategic settlement involved in maritime trade.
- Detailed topographical study and drone images have helped in identifying an early historic settlement surrounded by a fortification and the possibility of a moat encircling it.
- The excavations carried out in the already leveled area revealed elliptical, circular and rectangular brick structures.
- The most outstanding discovery is of massive sized brick enclosure wall at the southern part of the mound. This structure is of baked bricks and exposed to a length of more than 75 meters with an average width of about 3.40 meters, which rise to a height of nearly 2 meters and runs in a curvilinear pattern towards the northern end of the mound.
- The excavation revealed the presence of brick-built structures in different sizes and forms.
- The available brick sizes (43 – 48 cms) are comparable with the Satavahana / Ikshvaku period structures in Krishna valley i.e. Amaravati and Nagarjunakonda. On the basis of the brick size and associated findings they can be placed anywhere between 2nd – 1st century BCE or little later (nearly 2000 years old).
Antiquities Excavated
- Stone Vishnu Idol : Excavations conducted around the image revealed it to be a life size image of Vishnu measuring about 2 meters in height. It displays a four-armed Vishnu standing over a pedestal carrying chakra and conch in his upper right and left hands respectively. The lower right is in bestowing boon and the left hand in katihastha (resting on the hip) posture. The iconographical feature like the elaborate head gear, thick holy thread and decorative drapery dates it to Pallava period (circa 8th cent. CE).
- Other interesting antiquity retrieved is the molded female terracotta figurine with two hands lifted upwards.
9 . GB Pant Institute of Himalayan Environment & Development
Context : Realizing the importance of the Indian Himalayan region and recognizing the need to study its ecology, Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Shri Prakash Javadekar approved the proposal of setting-up of a New Regional Centre of the GB Pant Institute of Himalayan Environment & Development at Ladakh.
About GB Pant Institute of Himalayan Environment & Development
- G.B. Pant National Institute of Himalayan Environment & Sustainable Development was established in 1988-89, during the birth centenary year of Bharat Ratna Pt. Govind Ballabh Pant, as an autonomous Institute of the Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change (MoEF&CC), Govt. of India, which has been identified as a focal agency to advance scientific knowledge, to evolve integrated management strategies, demonstrate their efficacy for conservation of natural resources, and to ensure environmentally sound development in the entire Indian Himalayan Region (IHR).
Objectives
- Undertake in-depth research and development studies on environmental problems of the Indian Himalayan Region (IHR)
- Identify and strengthen the local knowledge of the environment and contribute towards strengthening researches of regional relevance in the scientific Institutions, Universities/NGOs and Voluntary agencies working in the Himalayan region, through interactive networking
- Evolve and demonstrate suitable technological packages and delivery systems for sustainable development of the region in harmony with local perceptions
The setting-up of this centre would ensure Institute’s Research & Development outreach in entire Trans Himalayan zone of Indian Himalaya by way of targeting following objectives:
- To promote alternative and innovative livelihoods for climate change vulnerable cold-desert communities;
- To facilitate conservation of critical/important cold desert habitats and biodiversity;
- To strengthen and establish approaches for addressing issues of water scarcity and
- To foster climate smart communities in the trans-Himalayan landscape
10 . Intensified Mission Indradhanush (IMI)
Background
- Immunization Programme in India was introduced in 1978 as ‘Expanded Programme of Immunization’ (EPI) by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India.
- In 1985, the programme was modified as ‘Universal Immunization Programme’ (UIP) to be implemented in phased manner to cover all districts in the country by 1989-90 with the one of largest health programme in the world. Despite being operational for many years, UIP has been able to fully immunize only 65% children in the first year of their life.
Mission Indradhanush
- To strengthen and re-energize the programme and achieve full immunization coverage for all children and pregnant women at a rapid pace, the Government of India launched “Mission Indradhanush” in 2014.
Goal of Mission Indradhanush
- The ultimate goal of Mission Indradhanush is to ensure full immunization with all available vaccines for children up to two years of age and pregnant women.
- The Government has identified 201 high focus districts across 28 states in the country that have the highest number of partially immunized and unimmunized children.
- Earlier the increase in full immunization coverage was 1% per year which has increased to 6.7% per year through the first two phases of Mission Indradhanush. Four phases of Mission Indradhanush have been conducted till August 2017 and more than 2.53 crore children and 68 lakh pregnant women have been vaccinated.
Intensified Mission Indradhanush (IMI)
- To further intensify the immunization programme Govt launched the Intensified Mission Indradhanush (IMI) in 2017.
- Government of India aims to reach each and every child up to two years of age and all those pregnant women who have been left uncovered under the routine immunisation programme/UIP.
- It would be reviewed by the Cabinet Secretary at the National level and will continue to be monitored at the highest level under a special initiative ‘Proactive Governance and Timely Implementation (PRAGATI)’.
- Intensified Mission Indradhanush will cover low performing areas in the selected districts (high priority districts) and urban areas.
- Special attention will be given to unserved/low coverage pockets in sub-centre and urban slums with migratory population. The focus is also on the urban settlements and cities identified under National Urban Health Mission (NUHM).
- Through Universal Immunization Programme, Government of India is providing vaccination free of cost against vaccine preventable diseases include diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, polio, measles, severe form of childhood tuberculosis, hepatitis B, meningitis and pneumonia (Hemophilus influenza type B infections), Japanese encephalitis (JE) in JE endemic districts with introduction of newer vaccines such as rotavirus vaccine, IPV, adult JE vaccine, pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) and measles-rubella (MR) vaccine in UIP/national immunization programme.
11. Facts for Prelims
Future Investment Initiative & Public Investment Fund
- The Future Investment Initiative (FII) is an international platform for expert-led debate between global leaders, investors and innovators with the power to shape the future of global investment. It is focused on utilizing investment to drive growth opportunities, enable innovation and disruptive technologies, and address global challenges.
- The Public Investment Fund seeks to become one of the largest and most impactful sovereign wealth funds in the world, enabling the creation of new sectors and opportunities that will shape the future global economy, while driving the economic transformation of Saudi Arabia. To achieve this, the Fund is building a world-class, diversified portfolio through investments in attractive, long-term opportunities across sectors and asset classes at both the domestic and international level. Working alongside global strategic partners and renowned investment managers, PIF acts as the Kingdom’s main investment arm to deliver a strategy focused on achieving attractive financial returns and long-term value for the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, in line with Vision 2030.
e-office
- e-Office aims to usher in more efficient, effective and transparent inter-government and intra-government transactions and processes. It enhances transparency, assure data security and data.