PIB Analysis for UPSC CSE
Topics Covered
- Small Farmer Agri – Business Consortium
- Scheme implemented by govt for reduction of farm logistic cost
- Price Rise of Onion
- CONFONET
- Changes in the definition of kilogram
- Economic Census
- National Centre for Sustainable Coastal Management
- National Afforestation Programme
- Anemia Mukt Bharat
- Hygiene Rating Scheme
- International Geological Congress
- Clean Ganga Fund
- Sustainable Development Cell
- Facts for Prelims
1 . Small Farmers’ Agri-Business Consortium (SFAC)
About SFAC
- The Government established Small Farmers’ Agri-Business Consortium (SFAC) as a Society in 1994 to facilitate agri-business ventures by catalyzing private investment through Venture Capital Assistance (VCA) Scheme in close association with financial institutions.
- The setting up of State level SFAC as counterpart agency of Central SFAC for agribusiness projects was part of the Scheme. The Scheme envisaged a corpus contribution from Central SFAC of Rs. 50.00 lakh to each State which establishes a State Level SFAC.
Functions of SFAC
- Promotion of development of small agribusiness through VCA scheme;
- Helping formation and growth of Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) / Farmer Producer Companies (FPCs);
- Improving availability of working capital and development of business activities of FPOs/FPCs through Equity Grant and Credit Guarantee Fund Scheme;
- Implementation of National Agriculture Market (e-NAM) Electronic Trading platform.
Schemes implemented by SFAC
Agri-Business Development (ABD) through Venture Capital Assistance (VCA) and Project Development Facility (PDF).
- The Scheme aims to facilitate the promotion of agri-business projects establishing backward linkages with farmers, providing assured market to their produce, thereby generating employment and enhancing farmers’ income.
Equity Grant and Credit Guarantee Fund Scheme for Farmer Producer Companies:
The scheme has two components :-
- A grant of upto Rs. 10.00 lakh to each registered Farmer Producer Company is given to match the member equity raised by the institution. This enhances the equity base of the FPC and enable it to approach financial institutions for raising working capital.
- Credit Guarantee Fund (CGF) has been set up in SFAC with a corpus of Rs. 100.00 Crores. The CGF will offer a cover of 85% to loans extended by banks to Farmer Producer Companies without collateral, upto a maximum of Rs. 1.00 Crore.
2 . Scheme implemented by govt for reduction of farm logistic cost
Initiatives undertaken
- Government has announced for development and upgradation of existing rural haats into Gramin Agricultural Markets (GrAMs). This will provide farmers facility to make direct sale to consumers and bulk purchasers which will reduce the logistic cost.
- The Government is providing support to farmers for development of agricultural marketing infrastructure in the country through the scheme of “Agricultural Marketing Infrastructure (AMI)”, which is a sub-scheme of Integrated Scheme for Agricultural Marketing (ISAM). Under AMI Scheme, Refrigerated Van as a transport vehicle is eligible for subsidy assistance for Integrated Value Chain (IVC) projects.
- Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) provides assistance for development of post harvest management and marketing infrastructure such as cold storage facilities, ripening chamber, pack houses, reefer vehicles to farmers to improve marketability of their produce.
- In order to develop the infrastructure in farming sector including that of distribution logistics, the Government is implementing Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana-Remunerative Approaches for Agriculture and Allied Sector Rejuvenation (RKVY-RAFTAAR) Scheme.
- Government has introduced National Agriculture Market (e-NAM) scheme wherein trading of agriculture and horticulture commodities is carried out by transparent price discovery method for produce of farmers through competitive online bidding system. A logistic module has been provided on e-NAM platform to provide efficient logistic facility for inter-mandi and inter-state trade on e-NAM platform.
- The Government has formulated and released model Agricultural Produce and Livestock Contract Farming & Services (Promotion & Facilitation) Act, 2018 which will facilitate reduction in supply chain for optimizing logistics.
3 . Price Rise of Onion
About Onion Crisis
- Onion is a seasonal crop with harvesting period of Rabi (March to June), Kharif (October to December) and late Kharif (January to March).
- In the intervening period (July to October), the market is fed by stored Rabi onions. During 2019-20, there was a 3-4 weeks delay in sowing as well as decline in sown area of the Kharif onion because of late arrival of monsoon.
- Further, untimely prolonged rains in the major growing States of Karnataka, Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh during the harvesting period, i.e., September/October, caused damage to the standing crops in these regions.
- All this adversely impacted production and quality of the Kharif crop. The rains during September/October also affected transportation of the crop from these regions to consuming areas. This led to limited availability of Kharif onion in the market and put pressure on its prices.
Steps taken by Govt
- Several steps such as creation of onion buffer of about 57,373 MT during Rabi 2019, withdrawal of incentive on export of onions under Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS), imposition of Minimum Export Price (MEP) and subsequent ban on exports of onions, facilitation of import, imposition of stock limit on onion traders, approval for import on onion through MMTC and domestic procurement of onions from producing/surplus States by NAFED for supplies in deficit States etc.
4 . CONFONET
About CONFONET
- Confonet stands for Computerization and Computer Networking of Consumer Fora in Country. It is an internet based Case Monitoring System developed for automating the work flow of the consumer forums, starting from case registration until announcement of judgment.
- The CONFONET project has been implemented in the backdrop of The Consumer Protection Act, 1986. Under the provision of the Act, quasi-judicial machinery, namely, Consumer Forums at the district level and Consumer Dispute Redressal Commissions at the State and National Level were setup.
Objectives
- The project aims at improving operational efficiency, co-ordination, accessibility, speed in judicial administration and to set Information Communication Technology (ICT) infrastructure at Consumer Redressal forums all over India. It aims at providing:
- E- Governance
- Efficiency
- Transparency
- Systematizing of working
- To achieve time bound delivery of justice to the consumers
5 . Changes in the definition of Kilogram
Background
- Kilogram was defined by the weight of a platinum-based ingot called “Le Grand K” which is locked away in a safe in Paris.
- Researchers met at Versailles voted to get rid of it in favour of defining a kilogram in terms of an electric current.
- The kilogram joined other standard units of measure such as the second, metre, ampere, Kelvin, mole and candela that would no longer be defined by physical objects.
- The kilogram now hinges on the definition of the Planck Constant, a constant of nature that relates to how matter releases energy.
Why it Changed
- The official object that defines the mass of a kilogram is a tiny, 139-year-old cylinder of platinum and iridium that resides in a triple-locked vault near Paris.
- Because it is so important, scientists almost never take it out; instead they use copies called working standards. But the last time they did inspect the real kilogram, they found it is roughly five parts in 100 million heavier than all the working standards, which have been leaving behind a few atoms of metal every time they are put on scales.
- This is one of the reasons the kilogram may soon be redefined not by a physical object but through calculations based on fundamental constants.
- In a world where accurate measurement is now critical in many areas, such as in drug development, nanotechnology and precision engineering – those responsible for maintaining the international system had no option but to move beyond Le Grand K to a more robust definition
What is the new system
- Electromagnets generate a force. Scrap-yards use them on cranes to lift and move large metal objects, such as old cars.
- The pull of the electromagnet, the force it exerts, is directly related to the amount of electrical current going through its coils. There is, therefore, a direct relationship between electricity and weight.
- So, in principle, scientists can define a kilogram, or any other weight, in terms of the amount of electricity needed to counteract the weight (gravitational force acting on a mass).
Plank’s Constant
- There is a quantity that relates weight to electrical current, called Planck’s constant – named after the German physicist Max Planck and denoted by the symbol h.
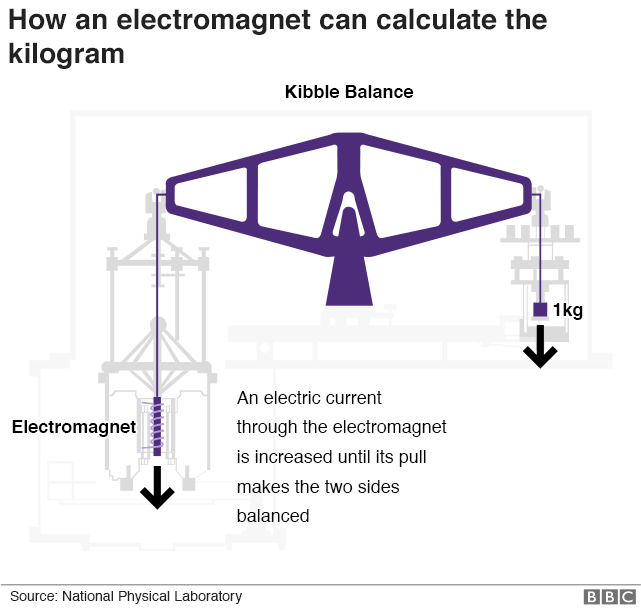
- But h is an incredibly small number and to measure it, the research scientist Dr Bryan Kibble built a super-accurate set of scales.
- The Kibble balance, as it has become known, has an electromagnet that pulls down on one side of the scales and a weight – say, a kilogram – on the other.
- The electrical current going through the electromagnet is increased until the two sides are perfectly balanced.
- By measuring the current running through the electromagnet to incredible precision, the researchers are able to calculate h to an accuracy of 0.000001%.
- This breakthrough has paved the way for Le Grand K to be deposed by “die kleine h“.
Kibble Balance
- Kibble balance is a self-calibrating electromechanical balance and provides the measurements of mass, traceable in terms of electrical parameters and provides linkage of macroscopic mass to the Planck constant(h).
6 . Economic Census
Context : The Seventh Economic Census was launched in the National Capital Territory of Delhi on Friday. The Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation (MoSPI) has tied up with Common Service Centre (CSC), an SPV under Ministry of Electronics and IT, to carry out the 7th National Economic Census.
About Economic Census
- The process of Economic Census was first held in 1978. This is the Seventh Census which will provide disaggregated information on various operational and structural aspects of all establishments in the country.
- The census will provide valuable insights into geographical spread/clusters of economic activities, ownership pattern; persons engaged etc. of the establishments engaged in economic activity.
- In the 7th Census, an IT based digital platform is being used for data capture, validation, report generation and dissemination will be used.
7th Economic Census has been conceived to provide:
- A nation‐wide Business Register as per international practices adopted by developing countries and in line with UNSD recommendations.
- Detailed information on economic variables, activity wise, of all the non‐ agricultural establishments of the country including its distribution at all India, State, district, village/ward levels for comprehensive analysis of the structure of the economy;
- Information on establishments registered under MSME Development Act, their assets and other economic criteria;
- Information on number of workers working in establishments (which are under operation), activity wise and area wise on;
- List of all establishments, tagged by geographical location up to village/ward level for local level planning purposes;
Scope and coverage proposed for 7th Economic Census
- All households/ establishments engaged in non‐agricultural economic activities including construction, except public administration, defense and compulsory social security are proposed to be covered in the 7th Economic census . Once the model of conduct of the 7th EC stabilizes, the scope can be enhanced to include these sectors from the 8th Census onwards.
- All households and establishments are proposed to be covered in the 7th Economic Census. Enumeration blocks of Population Census 2011 will form the primary geographical unit. Out of these.
- One of the main aims of the Economic Census is preparation of a National Business Register which can be linked with existing databases at the central and state government level. It is also proposed to have in place a threshold turnover in monetary terms for such households/ establishments for inclusion in the coverage of the Census.
- Establishments with fixed structures are proposed to be covered at the place of their operation. On the other hand, economic activities that are carried out without any fixed
7 . National Centre for Sustainable Coastal Management
Context : The Ministry set up the National Centre for Sustainable Coastal Management (NCSCM), Chennai to undertake studies and research in the area of Coastal Zone Management including coastal resources and environment.
The aims and Objectives of the Center are:
- Strive for being a World Class Knowledge Institution related to coastal zones, environment, resources and processes,
- To promote integrated and sustainable management of the coastal and marine areas in India for the benefit and wellbeing of the traditional coastal and island communities, and
- Advice the Union and State Governments and other associated stakeholder(s) on policy, and scientific matters related to Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM).
The six (06) research divisions of the NCSCM are: Geospatial Sciences, Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems (GIS), Integrated Social Sciences & Economics, Coastal environmental impact assessment, Conservation of Coastal & Marine Resources, Knowledge, Governance and Policy, and Futuristic Research and Integrated Island Management Unit.
Initiatives undertaken by NCSCM
- NCSCM is partnering with leading national and international research institutions and agencies through advanced research, networking, scientific committees and peer reviewed publications in international journals.
- NCSCM is mandated to disseminating knowledge pertaining to coastal management by capacity building at all levels for the benefit of coastal communities and stakeholders.
- NCSCM’s Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM) Plan has been developed on international standards that can be replicated in other parts of the World. Science based knowledge on coastal management developed by the Centre is used extensively for policy decisions.
- For the first time, Integrated Island Management plans including holistic island development plans have been prepared by NCSCM for implementation by coastal States/ UTs. NCSCM’s cutting-edge research infrastructure provides for world class research outputs and decision support system that directly enables policy decisions. NCSCM’s state-of-the-art laboratory facility provide an excellent opportunity to other Indian universities, Research Institutes, Government agencies for a collaborative research with NCSCM in the field of integrated coastal management.
- Survey of India and NCSCM have mapped the Hazard Line for the entire coast of India, which includes vulnerability mapping of flood, erosion and sea level rise. The outputs will be used by all the coastal States and UTs in managing coastal vulnerability in the coming years and as a tool for preparation of disaster management plans.
8 . National Afforestation Programme
Background
- The conservation and development of forest primarily involves three strategies – afforestation through natural/artificial regeneration, protection and management.
- The ministry is implementing three major schemes for development of forest areas
- National Afforestation Programme (NAP) scheme
- National Mission for a Green India (GIM)
- Forest Fire Prevention & Management Scheme (FFPM)
- NAP is being implemented for afforestation of degraded forest lands, GIM aims at improving the quality of forest and increase in forest cover besides cross sectoral activities on landscape basis. The FFPM takes care of forest fire prevention and management measures.
- For scientific management of forests, the States prepare management plan called Working Plan which highlights various activities to be undertaken in a forest division for effective management of forest. The working plan is approved by the Ministry.
- Besides, the funds collected under Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA), as compensatory levies from states inter-alia, is also used in plantation activity including compensatory afforestation by States/UTs.
About National Afforestation Programme
- The overall objective of the National Afforestation Programme (NAP) scheme is ecological restoration of degraded forests and to develop the forest resources with peoples’ participation, with focus on improvement in livelihoods of the forest-fringe communities, especially the poor.
- NAP aims to support and accelerate the on-going process of devolving forest conservation, protection, management and development functions tothe Joint Forest Management Committees (JFMCs) at the village level, which are registered societies.
- The scheme is implemented by three tier institutional setup through the State Forest Development Agency (SFDA) at the state level, Forest Development Agency (FDA) at the forest division level and JFMCs at village level.
Major Components
- The major components of the scheme includes afforestation under Seven plantation models, maintenance of previous years plantations and Ancillary Activities like soil and moisture conservation activities (SMC), fencing, overheads, monitoring and evaluation (M&E), micro-planning, awareness raising, Entry Point Activities (EPA) etc.
Other Features of the Scheme
- The Scheme is demand driven and afforestation area is sanctioned on the basis of past performance, potential degraded forest land available for eco-restoration and availability of budget. The Annual Plan of Operation (APO) of SFDAs is approved as per Guidelines of NAP.
- NAP is a centrally sponsored scheme which is implemented with the fund sharing pattern of 60: 40 percent between Centre and States wherein the sharing pattern for Northeastern and hilly States is 90:10.
- The central share of funds are released through State Government and state government transfers the funds to SFDA along with its state share which sometime causes delay in fund availability to SFDAs for implementation of NAPcausing delay in submission of mandatory documents for subsequent release of funds.
9 . Anemia Mukt Bharat
Background
- Considering, the slow progress i.e. less than 1% per annum in reduction of anaemia from 2005 to 2015, the Government of India has launched the Anemia Mukt Bharat (AMB) strategy under the Prime Minister’s Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nourishment (POSHAN) Abhiyaan and the targets has been set to reduce anaemia by 3% per year.
About the Strategy
- The 6x6x6 strategy under AMB implies six age groups, six interventions and six institutional mechanisms.
- The strategy focuses on ensuring supply chain, demand generation and strong monitoring using the dashboard for addressing anemia, both due to nutritional and non-nutritional causes.
- The six population groups under AMB strategy are :
- Children (6-59 months)
- Children (5-9 years)
- Adolescents girls and boys (10-19 years)
- Pregnant women
- Lactating women
- Women of Reproductive Age (WRA) group (15-49 years)
- The six interventions are :
- Prophylactic Iron and Folic Acid Supplementation
- Deworming
- Intensified year-round Behaviour Change Communication (BCC) Campaign and delayed cord clamping
- Testing of anaemia using digital methods and point of care treatment,
- Mandatory provision of Iron and Folic Acid fortified foods in Government funded health programmes
- Addressing non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies and fluorosis and the six institutional mechanisms.
- The six institutional mechanisms are :
- Inter-ministerial coordination
- National AnemiaMukt Bharat Unit
- National Centre of Excellence and Advanced research on Anemia Control
- Convergence with other ministries
- Strengthening supply chain and logistics
- AnemiaMukt Bharat Dashboard and Digital Portal- one-stop shop for Anemia.
10 . Hygiene Rating Scheme
About the Scheme
- FSSAI’s Hygiene Rating Scheme is a user driven, technology-enabled scheme applicable to food businesses supplying food directly to consumers either on or off the premise.
- Food businesses are rated on the basis of food hygiene and safety conditions found at the time of inspection and are given a score between (five to one) as per their hygiene and food safety compliance.
- This scheme has been recently introduced for food service sector such as hotels & restaurants, cafeterias, etc.
The main purpose of this scheme is to :
- Allow consumers to make an informed food choice about where to eat and inculcate right eating habits.
- Encourage food businesses to adopt high hygiene standards and to sustain them so as to showcase the same to their consumers.
11 . International Geological Congress
About International Geological Congress
- International Geological Congress (IGC) is the prestigious global platform for advancement of Earth Science.
- The first session of IGC assembled in 1878 in France with an aim to provide the global geological community with an opportunity to create an organizational framework for meeting at regular intervals.
- It envisaged a spirit of fraternal cooperation that transcends boundaries, languages and has the ability to bring together the geoscientific community across the continents and oceans.
- Founded as a non-profit scientific and educational organization in 1878, IGC came under the aegis of International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) in 1961. Since then the meetings of IGC are held in collaboration and under scientific sponsorship of IUGS
36th IGC congress
- Since the inception of IGC, 35 Congresses have been hosted by 24 countries throughout the world at 3 to 5-year intervals.
- India is gearing up to host the 36th International Geological Congress (IGC) in the capital during the first week of March next year.
- The theme of the forthcoming conference is ‘Geosciences: The Basic Science for a Sustainable Development’.
- Popularly described as the Olympics of Geosciences, the IGCs are a prestigious global geoscientific events participated by around 5000-6000 geoscientists from all across the world.
12 . Clean Ganga Fund
About Clean Ganga Fund
- The Clean Ganga Fund was established as a Trust under the Indian Trusts Act, duly approved by the Union Cabinet and with the Union Finance Minister heading the Board.
- Domestic donors to the CGF are eligible for 100% income tax exemption under Section 80 G (1) (i) of the Income Tax Act 1961. Contributions to CGF also fall within the purview of CSR activity as defined in Schedule VII to the Companies Act, 2013.
Features of the Fund
- CGF will have the objective of contributing to the national effort of improving the cleanliness of the river Ganga with the contributions received from the residents of the country, NRIs/ PIO and others.
- CGF will be operated through a bank account by a Trust.
- Foreign donors could get suitable tax exemptions in domestic law, wherever permissible.
- CGF will explore the possibility of setting up daughter funds in other jurisdictions/countries of high donor interest such as USA, UK, Singapore, UAE, etc. to enable tax benefits to donors in their respective jurisdictions.
- CGF will be catalytic in nature and will identify and fund specific projects which could be pilot projects, R&D projects, innovative projects or other focused projects. The Fund will define specific and measurable objectives to form the basis for planning, funding, and evaluation.
Activities to be financed with the Fund:
- Activities outlined under the ‘Namami Gange’ programme for cleaning of river Ganga.
- Control of non-point pollution from agricultural runoff, human defecation, cattle wallowing, etc.
- Setting up of waste treatment and disposal plants along the river around the cities.
- Conservation of the biotic diversity of the river.
- Community based activities to reduce polluting human interface with the river.
- Development of public amenities including activities such as Ghat redevelopment.
- Research and Development and innovative projects.
- Research and Development projects and innovative projects for new technology and processes for cleaning the river.
- Independent oversight through intensive monitoring and real time reporting.
- Any other activity as approved by the Trust.
13 . Sustainable Development Cell
Context : The Ministry of Coal has decided to establish a ‘Sustainable Development Cell’ in order to promote environmentally sustainable coal mining in the country and address environmental concerns during the decommissioning or closure of mines. This move gains significance as the new private entities are now going to form a significant part of the future, a set of guidelines for proper rehabilitation of mines need to be evolved in tune with global best practices.
Role of Sustainable Development Cell
- The Sustainable Development cell (SDC) will advise, mentor , plan and monitor the mitigation measures taken by the coal companies for maximising the utilisation of available resources in a sustainable way, minimising the adverse impact of mining and mitigating it for further ecosystem services and will act as nodal point at Ministry of Coal level in this matter.
- This cell will also formulate the future policy framework for the environmental mitigation measures including the Mine closure Fund.
Tasks of the Cell
- The SDC will adopt a systemic approach, starting from collection of data, analysis of data, presentation of information, planning based on information; by domain experts, adoption of best practices, consultations, innovative thinking, site-specific approaches, knowledge sharing and dissemination and finally end with an aim to ease the lives of people and communities in general. All of the above will be done by executing following tasks on a planned way:
- Land amelioration and afforestation:
In India approximately 2,550 sq Km areas is under different coal mines and there are also plans to bring more areas under it. These land masses required both extensive and intensive amelioration measures and will be carried out as per following procedure:
- Collection of all the baseline data/maps related to different coal mines like total mines/ block areas, OB dumps areas, water filled voids, reclaimed areas, unutilized areas, plantations etc., from various Coal companies. All the data/maps will be collated and analysed on a GIS based platform and different thematic information and maps will be prepared. These will be updated at regular intervals. All GIS based activities will be carried out with active participation of CMPDIL.
- To help Coal companies to identify areas where plantation projects could be taken up immediately, along with identification of various species of plants, suitable for specific regions to create large carbon sinks for climate change management.
- To Identify the activities to be taken up for creation of additional land suitable for plantation, stabilization of slope, soil treatment, creation of levelled land, de-watering etc., as per time line under MCP.
- It also checks the possibility and plan for productive reuse of these lands for rehabilitation, integrated modern township, agriculture, horticulture, FCA compensatory land, renewable energy farms etc.
2. Air quality, emission and noise management:
- To advice coal companies for effective implementation of environmental mitigation measures (water sprinkling, dust suppression methods, noise barriers etc.) related to air and noise pollution generated due mine activities, heavy earth moving machines (HEMMs), transport of coal etc.
- It also works towards energy efficiency in the mining operation, noise and emission reduction in case of HEMMs.
- Analysis of Environment Management Plans (EMP) of different companies and will advise coal companies to making it more effective.
3. Mine water management:
- Collection of data regarding present quantity, quality, surface runoff, drainage of mine water, future availability of water collected in UG or OC coal mines etc., and to analyse it on a GIS based platform to prepare model Coal Mine Water Management Plans (CMWMP).
- The plan will suggest ways and also have innovative planning to storage, treatment and re-use of such water for drinking, irrigation, fisheries, tourism, industrial or any other sustainable purpose.
4. Sustainable Overburden Management:
- The cell will also check feasibility and suggest measures to reuse, recycle and rehabilitation of over burdened dumps in a sustainable manner.
- Will examine and plan out use of overburdened material for use in different infrastructure projects, earthen bunds etc.
5. Sustainable Mine Tourism:
- To explore and conceptualise a plan for the beautification & creation of eco parks in the reclaimed areas and which will also include water bodies etc., for re-creation activities and tourism purpose. It will also explore tourism potential and plan it out in few underground mines.
6: Planning and Monitoring:
- Analysis of Mine Closure Plans (MCP)of different companies and advise to make it more effective.
- To help Coal companies to finalize time- line for execution of different mitigation activities / projects in all mines in phased manner.
- Will also monitor effective utilization of Mine Closure Fund and Environment Budgets of Different Coal Companies.
- To formulate future guidelines for the mine closure plan, mine closure fund etc.
7: Policy, Research, Education, and Dissemination:
- Will hire experts/ institutions/ organisations to conduct specific studies for establishing a robust knowledge base.
- Will organise consultative meetings, workshops, field visits, exposure study tours etc., to enrich the knowledge base, known best global and ideas for environmental mitigation planning and monitoring.
- Will conduct regular workshop and seminar for the company level officials to educate them in new methods, technologies, approaches and also global practices.
14 . Facts for Prelims
White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) and Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus(IHHNV)
- White spot syndrome virus (WSSV) is highly virulent and has caused significant production losses to the shrimp culture industry over the last decade.
- Infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) also infects penaeid shrimp and, while being less important than WSSV, remains a major cause of significant production losses
National energy conservation awards
- The National Energy Conservation Awards Programme recognizes the energy efficiency achievements in 56 sub sectors across industry, establishments and institutions such as thermal power stations, office and BPO buildings, hotels, hospitals, shopping malls, zonal railways, railway workshops and stations, municipalities, State Designated Agencies and manufacturers of BEE Star labeled appliances/equipment and electricity distribution companies.
- As part of its awareness outreach, every year on the national conservation day, BEE recognizes and encourages endeavors of industries and other establishments in reducing energy consumption by felicitating them with National Energy Conservation Awards. Apart from it, BEE also felicitates prizes to the winners of National Painting Competition on Energy Conservation.
Hathkargha Samvardhan Sahayata (HSS)
- Hathkargha Samvardhan Sahayata (HSS) was introduced on 1st December 2016 with an objective to provide looms/accessories to the weavers to enhance their earnings through improved productivity and quality of the handloom products.
- Under the scheme, 90% of the cost of loom/accessory is borne by the Government of India while remaining 10% is borne by the beneficiary.
- The Government of India’s share is released directly in the Bank account of the beneficiary through designated agency.
Rohne and Tokisud Mines
- Rohne and Tokisud mines are situated in Hazaribagh District of Jharkhand.
National Safety Awards
- The National Safety Awards (N.S.A) was instituted in the year 1965, NSA is meant to give recognition to good safety performance on the part of Industrial Establishments and to maintain the morale of both the managements and the workers for accident prevention and safety promotion programmes.
- Initially the NSA was instituted for factories registered under the Factories Act, 1948 which work One million man-hours or more during the contest year.
- From the year 1971, separate schemes were introduced for factories working less than One million manhours and also for Ports.
- From the year 1978 two more schemes were introduced for factories working more than one lakh and less than two and half lacs manhours during each year of the contest period.
- Further, the schemes which existed prior to 1978 were modified in 1978 as per the decision of the Awards Committee specially constituted for this purpose by the Ministry of Labour and Employment, Govt. of India. At present there are twelve schemes
- These schemes are operated by the Directorate General Factory Advice Service and Labour Institutes (DGFASLI), Mumbai, under the Ministry of Labour and Employment, Government of India.
Vijay Diwas
- Vijay Diwas is commemorated every 16 December in India, to Indian military’s victory over Pakistan in Indo-Pakistani War of 1971 for the liberation of Bangladesh from Pakistan.
- The end of the war also resulted in the unilateral and unconditional surrender of the Pakistan Army and subsequent secession of East Pakistan into Bangladesh.
Finance Commission
- The Finance Commission, set up under Article 280 of the Constitution, basically decides how revenue has to be distributed between the Centre and the States.
- In addition, the Commission also decides the principles on which grants-in-aid will be given to the States.
- The 15th Finance Commission was constituted on November 27, 2017 and is headed by former Revenue Secretary and former Rajya Sabha MP N.K. Singh.
- The recommendations, to be observed for a period of five years, will kick in from April 1, 2020.
Joint Military Exercise Surya Kiran – XIV
- Exercise SURYA KIRAN-XIV is a joint military training exercise between India and Nepal
- The exercise of this year culminated at Nepal Army Battle School (NABS), Salijhandi, Rupendehi district of Nepal, wherein the troops of both the Armies participated in 14 days long joint training based on counter insurgency operations in jungle and mountainous terrain and also practised response mechanism in the eventualities of natural and man made disasters.