Daily Current Affairs for UPSC CSE
Topics Covered
- 5 G
- Swacchh Surveekshan Survey
- Study on Medical Fungi
- Swachh Surveekshan Grameen
- United Nations World Geospatial information Congress
- Card Tokenisation
- Facts for Prelims
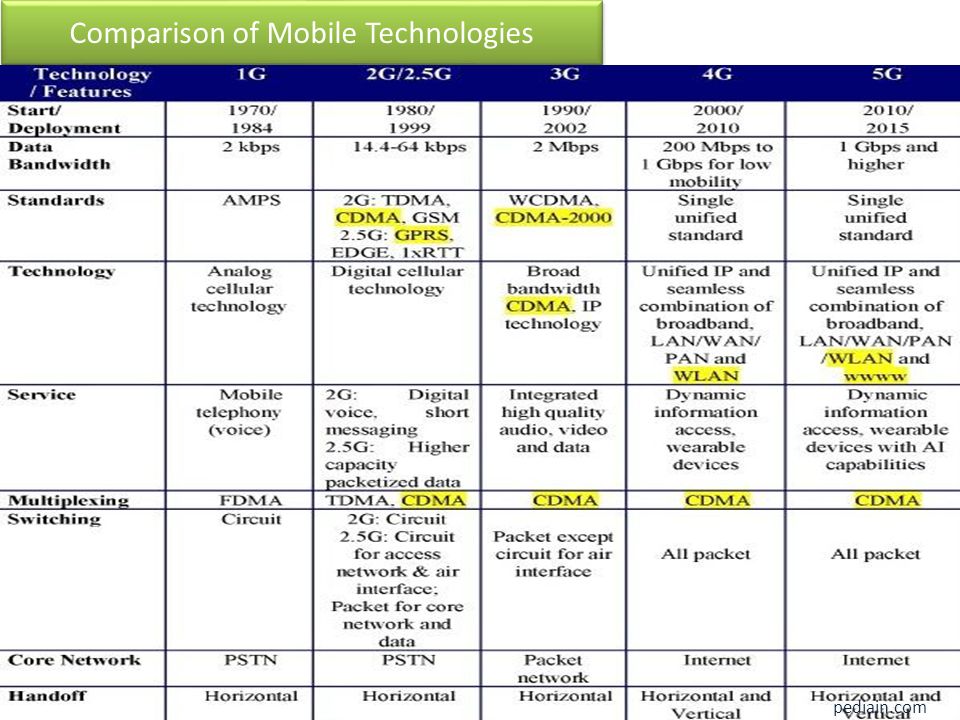
1 . 5 G Technology
Context: Mobile phone users in the country will soon be able to experience ultra-high-speed Internet using 5G wireless technology, with Indian Prime Minister launching the next-generation mobile network.
About 5G technology
- 5G is the 5th generation mobile network. It is a new global wireless standard after 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G networks.
- 5G enables a new kind of network that is designed to connect virtually everyone and everything together including machines, objects, and devices.
- 5G wireless technology is meant to deliver higher multi-Gbps peak data speeds, ultra-low latency, more reliability, massive network capacity, increased availability, and a more uniform user experience to more users.
- Higher performance and improved efficiency empower new user experiences and connect new industries.
How Does 5G Work?
- Wireless communications systems use radio frequencies (also known as spectrum) to carry information through the air.
- 5G operates in the same way but uses higher radio frequencies that are less cluttered. This allows it to carry more information at a much faster rate.
- These higher bands are called ‘millimeter waves’ (mmwaves).
- They were previously unused but have been opened up for licensing by regulators.
- They had been largely untouched by the public as the equipment to use them was largely inaccessible and expensive.
- While higher bands are faster at carrying information, there can be problems with sending over large distances.
- They are easily blocked by physical objects such as trees and buildings.
- In order to circumvent this challenge, 5G will utilise multiple input and output antennae to boost signals and capacity across the wireless network.
- The technology will also use smaller transmitters. Placed on buildings and street furniture, as opposed to using single stand-alone masts. Current estimates say that 5G will be able to support up to 1,000 more devices per metre than 4G.
- 5G technology will also be able to ‘slice’ a physical network into multiple virtual networks. This means that operators will be able to deliver the right slice of network, depending on how it is being used, and thereby better manage their networks.
- This means, for example, that an operator will be able use different slice capacities depending on importance.
- So, a single user streaming a video would use a different slice to a business, while simpler devices could be separated from more complex and demanding applications, such as controlling autonomous vehicles.
- There are also plans to allow businesses to rent their own isolated and insulated network slice in order to separate them from competing Internet traffic.
Who Invented the Fifth Generation Network?
- The first nation to adopt on a large scale was South Korea, in April 2019, at which point there were some 224 operators in 88 countries around the world investing in the technology.
- In South Korea, all the 5G carriers used Samsung, Ericsson and Nokia base stations and equipment, apart from one who used Huawei equipment. Of these suppliers, Samsung was the largest, having shipped 53,000 base stations from a total of 86,000 base stations installed in the country at the time.
- There are currently nine companies that sell 5G radio hardware and systems for carriers. These are Altiostar, Cisco Systems, Datang Telecom, Ericsson, Huawei, Nokia, Qualcomm, Samsung and ZTE.
Differences between the previous generations of mobile networks and 5G
- The previous generations of mobile networks are 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G.
- First generation – 1G
- 1980s: 1G delivered analog voice.
- Second generation – 2G
- Early 1990s: 2G introduced digital voice (e.g., CDMA- Code Division Multiple Access).
- Third generation – 3G
- Early 2000s: 3G brought mobile data (e.g., CDMA2000).
- Fourth generation – 4G LTE
- 2010s: 4G LTE ushered in the era of mobile broadband.
- 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G all led to 5G, which is designed to provide more connectivity than was ever available before.
- 5G is a unified, more capable air interface. It has been designed with an extended capacity to enable next-generation user experiences, empower new deployment models and deliver new services.
- With high speeds, superior reliability and negligible latency, 5G will expand the mobile ecosystem into new realms.
- 5G will impact every industry, making safer transportation, remote healthcare, precision agriculture, digitized logistics — and more — a reality.
2 . Swacchh Surveekshan Survey
Context: Swachh Survekshan 2022 awards were given away by the Indian President as part of the Azadi@75 Swachh Survekshan 2022 hosted as part of the Swachh Bharat Mission. She also released the Swachh Survekshan 2022 dashboard.
About Swachh Survekshan
- Swachh Survekshan is an annual survey of cleanliness, hygiene and sanitation in cities and towns across India.
- It was launched as part of the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, which aimed to make India clean and free of open defecation by 2nd October 2019.
- The first survey was undertaken in 2016 and covered 73 cities; by 2020 the survey had grown to cover 4242 cities and was said to be the largest cleanliness survey in the world.
- In a bid to scale up the coverage of the ranking exercise and encourage towns and cities to actively implement mission initiatives in a timely and innovative manner, Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) is now in the process of conducting the sixth edition of the survey to rank all cities under Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban (SBM-U) with Quality Council of India (QCI) as its implementation partner.
Objectives
- The objective of the survey is to encourage large scale citizen participation, ensure sustainability of initiatives taken towards garbage free and open defecation free cities, provide credible outcomes which would be validated by third party certification, institutionalize existing systems through online processes and create awareness amongst all sections of society about the importance of working together towards making towns and cities more habitable and sustainable.
- Additionally, the survey also intends to foster a spirit of healthy competition amongst towns and cities to improve their service delivery to citizens and move towards creating cleaner cities.
How cities are Ranked
- Part 1 Service Level Progress (SLP) : Data provided by ULBs
- Part 2 Certification – Based on GFC Star rating, ODF+/ODF++/Water+
- Based on GFC Star rating, ODF+/ODF++/Water+ 5 components – Feedback, engagement, experience, Swachhta app, Innovation
- Final Score : Cities are ranked based on marks obtained from Part 1, Part 2 and Part 3
2022 Ranking
- Over the years, Swachh Survekshan (SS) has emerged as an effective tool for transforming the urban landscape. This year’s Survekshan participated by 4,355 cities, also saw an unprecedented number of citizens’ feedback – over 9 crores, compared to 5 cores last year.
- In all, 22 States and 5 UTs received awards, of whom 8 States received more than 10 awards each. 8 States and 5 UTs have shown improvements ranging between 5 – 25% in their overall ground level performance over last year.
- Of them, 4 out the 8 North Eastern states have shown significant improvement in the overall performance over the last year. Moreover, 10 Cantonment Boards (against 7 CBs last year) and 2 Ganga towns received awards.
- A heartening feature of the awards was that smaller cities with population of less than 25,000 have performed admirably in the survey, with 40 of them receiving awards today.
Details of the Ranking
- Indore has been adjudged the cleanest city of India for the sixth year in a row, while Madhya Pradesh is the cleanest State in the country.
- Surat is the second cleanest city and Navi Mumbai ranks a close third in the category of cities with a population of more than a lakh.
- In the population category of less than one lakh, Panchgani and Karad from Maharashtra bagged the first and third positions respectively, while Patan from Chhattisgarh bagged the second position.
- Tirupati received the best city award in Safai Mitra Suraksha category.
- Haridwar in Uttarakhand received the award for the best Ganga town in more than one lakh population cities.
- Bijnor ranked first among Ganga towns with less than one lakh population, followed by Kannauj and Garhmukhteshwar.
- Maharashtra’s Deolali was adjudged the country’s cleanest Cantonment Board.
- Shivamogga in Karnataka received the fast mover city award.
- The State awards saw Madhya Pradesh emerge as the Cleanest State in the category of “more than 100 Urban Local Bodies”, relegating Chhattisgarh, the cleanest State of the previous three years, to second place. Maharashtra emerged as third cleanest State.
- Tripura got the cleanest state award in the “less than 100 urban local bodies category”, dislodging Jharkhand, which had won in the last two consecutive years.
- Jharkhand and Uttarakhand received the second and third spots respectively.
- Indore further cemented its position by emerging as India’s first 7-star Garbage Free city, while Surat, Bhopal, Mysuru, Navi Mumbai, Vishakhapatnam, and Tirupati earned 5-star Garbage Free certifications.
3 . Study on Medical Fungi
Context: An analytical study of medicinal fungi carried out by researchers from the Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Chennai (IMSc), shows that some chemicals they secrete may find use as novel drugs.
About the research
- The researchers used a database, MeFSAT (Medicinal Fungi Secondary Metabolites And Therapeutics), which compiles information on 184 medicinal fungi, including mushrooms.
- The researchers analysed the structure of 1,830 secondary metabolites of medicinal fungi.
Fitness booster
- Secondary metabolites are chemical compounds that fungi produce when they are stressed. They enhance the fungus’ ability to survive. The work has been published in the preprint server BioRXiv.
- Cordycepin, a secondary metabolite produced by Cordyceps species of fungus, is known to have anti-tumour properties.
- Not only cordycepin, in general, several secondary metabolites are known to be beneficial for humans in terms of both therapy and health
Diverse structures
- In their analysis, the researchers found that the secondary metabolites were structurally distant from existing drugs.
- Also, their ‘scaffolding’ was different from known drugs.
- About 94% of the chemical scaffolds identified in secondary metabolites of medicinal fungi were not present in approved drugs.
- As for the complete chemical structure, the secondary metabolites were quite dissimilar to the approved drugs.
- This alone cannot tell that there are metabolites in fungi that can be used as drugs.
- However, the secondary metabolites of medicinal fungi have molecular properties, which are important for drug likeness, similar to approved drugs.
- This makes the secondary metabolites of the medicinal fungi suitable for identifying novel drugs with hitherto unknown chemical scaffolds.
Used in medicine
- Medicinal fungi belong to two taxonomic divisions namely, basidiomycota and ascomycota. Mushrooms belong to the basidiomycota division.
- An example is Agaricus bisporus, the button mushroom, which can be consumed.
- Fungi belonging to the ascomycota division are generally not mushrooms.
- In future, we plan to map the scaffolds to their biological targets, which will further pave the way for identifying potential lead molecules for drug discovery.
4 . Swachh Surveekshan Grameen
Context: Swachh Survekshan Gramin (SSG), 2022 was released recently which looks into the sanitation status of rural areas
About Swachh Survekshan Gramin (SSG)
- Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS) is implementing two flagship programmes of the central government i.e. Swachh Bharat Mission Grameen (SBM-G) and Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM).
- SBM-G was started on 2nd October 2014 with the aim to stop Open Defecation. On 2nd October 2019, all villages in the country declared themselves ODF. Thereafter, SBM-G 2.0 was launched in 2020 to sustain the ODF status in villages and improve the level of cleanliness in rural areas through Solid and Liquid Waste Management, thereby making villages ODF Plus.
- The Survekshan aimed to undertake ranking of States and Districts on the basis of their performance attained on key quantitative and qualitative SBM-G parameters and engage rural community in improvement of their sanitation status through an intensive and holistic IEC campaign and engage with select Gram Panchayats and citizens in every district.

Key highlights
- Telangana was ranked first for the cleanliness of its villages in the Swachh Survekshan Gramin (SSG), 2022.
- After Telangana, Haryana was placed second followed by Tamil Nadu in the Large States category.
- The Swachh Survekshan Gramin, 2022 award ranks States and districts on the basis of their performance attained on Swachh Bharat Mission Gramin (SBM-G) parameters and engagement of the rural community in improvement of their sanitation status.
- Among smaller States and Union Territories, Andaman and Nicobar secured the first position, followed by Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu and Sikkim.
- Golaghat district of Assam finished at the bottom of 709 districts, ranked in this survey.
- The two other worst performers were from Bihar – Banka and Katihar.
- Since Delhi and Chandigarh are fully urbanized UTs, these were not ranked.
- The status report on “Functionality Assessment of Tap Connections” under the Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) was also releaased.
- Burhanpur (Madhya Pradesh) receives a special award for being the first “Har Ghar Jal” certified district.
- The awards were given to commemorate the birth anniversary of Father of the Nation Mahatma Gandhi
Swachh Bharat Mission-Gramin
- Swachh Bharat Mission-Gramin is a movement to bring in behavioural change in population.
- The use of toilets, the habit of washing hands with soap and having water supply through taps acted as a shield for the country during the pandemic.
- Since the launch of SBM-G in 2014, over 11 crore toilets had been built and about 60 crore people had given up open defecation.
- The second phase of the mission, launched in 2020, aims to make all six lakh villages in India ‘Open Defecation Free Plus’.
- Having achieved success against open defecation, now the need is to address more complex and technical problems like solid and liquid waste management.
5 . United Nations World Geospatial Information Congress
Context: India’s geospatial technology industry was expected to cross ₹63,100 crore by 2025 at a growth rate of 12.8%, Union Science Minister said at briefing to announce the second United Nations World Geospatial Information Congress (UNWGIC) scheduled in Hyderabad from October 10-14.
Key highlights
- The conference is expected to be attended by over 2,000 delegates, including over 700 international delegates and participants from about 120 countries.
- It will also have participants from the Survey of India, a 255-year-old organisation, and senior officials, non-governmental organisations and academia.
- Rural Development Ministry had mapped over 45 lakh kilometres of rural roads by using 21 data layers of a digital map of India, to create digitised information regarding water bodies, green areas, plots, and other structures essential for administrative purposes.
- Nearly 2.6 lakh gram panchayat had been covered by the Ministry under the mapping and digitisation scheme.
- The Guidelines for Geospatial Data, the Drone Rules 2021, and the Draft Policies (Geospatial, Remote Sensing, and Satellite Navigation) would liberalise, democratise, and commercialise the use of geospatial data and information for planning and monitoring requirements within the country.
- Last year, India announced plans to prepare digital maps of all its 6,00,000 villages and pan-India 3D maps will be prepared for 100 cities.
- An ongoing scheme, piloted by the Ministry of Panchayati Raj, called SVAMITVA (Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas), was launched in April 2020 to digitise land records.
United Nations World Geospatial Information Congress (UNWGIC)
- United Nations Economic and Social Council, of which the Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management is a subsidiary body, “encouraged Member States to hold regular high-level, multi-stakeholder discussions on global geospatial information, including through the convening of global forums, with a view to promoting a comprehensive dialogue with all relevant actors and bodies”
- Aim of the United Nations World Geospatial Information Congress (UNWGIC) is to provide a convening, participatory and inclusive environment to enhance the communication, understanding, knowledge and application of geospatial information management.
- The inaugural United Nations World Geospatial Information Congress was held in Deqing, Zhejiang Province from 19 to 21 November 2018.
- The Second United Nations World Geospatial Information Congress in Hyderabad, India will be hosted by the Government of the Republic of India through its Ministry of Science and Technology. The Committee of Experts is expected to convene the third edition of the United Nations World Geospatial Information Congress in 2026.
Second United Nations World Geospatial Information Congress in Hyderabad
- Hosted by the Government of India through its Ministry of Science and Technology, the convening of the UNWGIC arises out of the mandate from the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) to the Committee of Experts to convene global forums to promote comprehensive dialogue on global geospatial information management with all relevant governments, international organizations and stakeholders.
- The congress will be a global event bringing together all stakeholders at the highest level to address and ensure that geospatial information has its widest and fullest utility in service of sustainable social, economic and environmental development.
- Theme: Geo-Enabling the Global Village: No one should be left behind
- The second UNWGIC will reflect the importance of integrated geospatial information to support sustainable development and the wellbeing of society, address environmental and climate challenges, embrace digital transformation and technological development, and catalyze vibrant economy.
- While the actual second UNWGIC program covers three days, the overall event will be a weeklong and will include global and regional meetings, workshops and learning events, expert meetings and side events, including the eleventh plenary meeting of the Regional Committee of United Nations Global Geospatial Information Management for Asia and the Pacific (UN-GGIM-AP), as well as the annual meeting of the UN-GGIM Expanded Bureau.
UN GGIM
- Recognizing the need to promote international cooperation in the field of global geospatial information, the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) established the United Nations Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management (UN-GGIM) with ECOSOC resolution 2011/24 entitled “Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management”.
- ECOSOC established the Committee of Experts as the apex intergovernmental mechanism for making joint decisions and setting directions with regard to the production, availability, and application of geospatial information within national, regional, and global policy frameworks.
- Led by Member States, the Committee aims to address global challenges regarding the use of geospatial information, including in the development agendas, and to serve as a body for global policymaking in the field of integrated geospatial information management.
6 . Card Tokenisation
Context : From October 1 the Reserve Bank of India’s card-on-file (CoF) tokenisation norms have kicked in, which aim at improved safety and security of card transactions. Now, for any purchases done online or through mobile apps, merchants, payment aggregators and payment gateways will not be able to save crucial customer credit and debit card details such as three-digit CVV and expiry date.
What is tokenisation?
- Tokenisation refers to the replacement of actual card details with a unique alternate code called the ‘token’, which shall be unique for a combination of card, token requester, (i.e. the entity which accepts requests from the customer for tokenisation of a card and passes it on to the card network to issue a corresponding token) and the device.
How did India decide to carry out tokenisation?
- In September 2021, the RBI prohibited merchants from storing customer card details on their servers with effect from January 1, 2022, and mandated the adoption of card-on-file (CoF) tokenisation as an alternative.
- Following a series of representations from several industry players and digital payment platforms who anticipated disruption in online transactions from January 1, 2022, the RBI extended the implementation date of card-on-file (CoF) tokenisation norms by another six months to June 30, 2022.
- The June 2022 deadline was further extended as the RBI felt that although considerable progress had been made in terms of token creation and transaction processing based on these tokens had also commenced, the concept was yet to gain traction across all categories of merchants. Subsequently, the deadline was extended till September 30, 2022.
But how will tokenisation work?
- A debit or credit card holder can get the card tokenised by initiating a request on the app provided by the token requester. The token requester will forward the request to the card network which, with the consent of the card issuer, will issue a token corresponding to the combination of the card, the token requester, and the device.
- “In case of an online transaction, instead of card details, a unique token will be stored on the server. The merchant or transaction platform sends out a message to Visa or Mastercard or a payment gateway, who asks for a token against that card number and will then pass it on to the bank for allowing the transaction,” NTT DATA Payment Services India CEO Dewang Neralla said.
- The customer will not be charged for availing the tokenisation service.
- Earlier, the facility for card tokenisation was available only for mobile phones and tablets of interested card holders. Subsequently, with an uptick in tokenisation volume, the RBI decided to extend the scope of tokenisation to include consumer devices – laptops, desktops, wearables (wrist watches, bands, etc.) and Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Who can offer tokenisation services?
- Tokenisation can be performed only by the authorised card network and recovery of original Primary Account Number (PAN) should be feasible for the authorised card network only. Adequate safeguards have to be put in place to ensure that PAN cannot be found out from the token and vice versa, by anyone except the card network. RBI has emphasised that the integrity of the token generation process has to be ensured at all times.
What do customers gain from tokenisation?
- A tokenised card transaction is considered safer as the actual card details are not shared with the merchant during transaction processing. Actual card data, token and other relevant details are stored in a secure mode by the authorised card networks.
- The token requestor cannot store Primary Account Number (PAN), or any other card details. Card networks are also mandated to get the token requester certified for safety and security that conform to international best practices/globally accepted standards.
- “With card tokenisation, a card and merchant specific token is generated. Going forward that token can be used for all online transactions with that merchant. This will ensure enhanced security. In case of any data breach or hacking attempt at the merchant’s end, the customer’s card details will be protected,
7 . Facts for Prelims
Laboratory for conservation of endangered species
- It is India’s only facility for conservation of endangered species.
- The Laboratory for the Conservation of Endangered Species (LaCONES) is a dedicated facility of CSIR’s Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB) in Hyderabad which uses modern biotechnologies for conservation of endangered wildlife.
- CCMB-LaCONES is the only laboratory in India that has developed methods for collection and cryopreservation of semen and oocytes from wildlife and successfully reproducing endangered blackbuck, spotted deer and Nicobar pigeons.
- Through this work, it has established Genetic Resource Bank for Indian wildlife.
- So far, genetic resources from 23 species of Indian wild animals have been collected and preserved.
- This facility would increase the collection of genetic resources from wildlife through collaboration with zoos in India.
- It would also facilitate exchange of genetic material between the Indian zoos for maintaining genetic diversity and conservation management made accessible to scientists and wildlife managers for implementing conservation programs.
Sharang guns
- The completely indigenous Sharang 155mm/45 calibre Gun system was indigenously developed with modification of Soltam 130 mm imported Russian Gun System at Gun Carriage Factory.
- Notable improvements with Sharang are the 45-caliber gun barrel chambered for 155mm ammunition.
- The breech loading mechanism was altered. The wheels supporting the carriage were changed and the trails–the twin “legs” for stabilizing the weapon’s recoil–were redesigned as well and made sturdier.
- The gun’s range has now gone from 27km to over 36km with the upgrade.
- The OFB claims the Sharang can strike targets up to 36 kilometers away without specifying if these mean firing conventional ammunition or rocket assisted projectiles.
- It has a striking range of 39 kilometres. It also has the more explosive capability and hence and more damage potential.
- The weapon system is simple to operate and maintain.
- The Sharang Towed gun is designed for worldwide service under all climatic conditions and can fire all existing standard 155-mm ammunition.
- This step will reduce the logistic trail of the Army as it does away with the need to carry 130mm shells and support equipment as the mainstay of the Army’s long-range artillery is 155mm guns.
Golden visa
- The Golden visa is a long-term residence visa which enables foreign talents to live, and work or study in the UAE while enjoying exclusive benefits.
- Investors, entrepreneurs, scientists, outstanding students and graduates, humanitarian pioneers and frontline heroes are amongst those eligible for the Golden visa.
- The UAE’s ‘Golden visa’ enables foreign talents to live and work or study in the UAE while enjoying exclusive benefits which include:
- an entry visa for six months with multiple entries to proceed with residence issuance
- a long term, renewable residence visa valid for 10 years
- a self-sponsored visa, as there is no need for an employment sponsor
- ability to stay outside the UAE for more than the usual restriction of six months in order to keep their residence visa valid
- sponsoring their family members, including spouse and children regardless of their ages
- sponsoring unlimited number of domestic helpers
- allowing family members to stay in the UAE until the end of their permit duration, if the primary holder of the Golden visa passes away.
Satellite Broadband service
- Satellite broadband is network connectivity provided through low-earth-orbit (LEO) or geostationary satellites, with the latter providing much faster data rates.
- Satellite broadband enables Internet access via satellite in two steps:
- A personal computer broadcasts requests via satellite modem to a satellite dish placed on top of a home or business.
- The dish sends and receives signals from the orbiting satellite. If the dish can get a clear view of the southern sky (over the United States), a user can receive satellite Internet access.
- Satellite broadband is also known as satellite Internet access
- The two biggest developments in the global satellite communication space are the emergence of LEO (low-earth orbit constellations) that promises to provide truly global coverage and lower latency service, and HTS (High Throughput Satellites Service) which offers unprecedented capacity and flexibility.
- Satellite broadband services can connect the most remote parts of the country which are otherwise difficult to connect through fibres.
- It can, therefore, help in addressing the need of the market for fibre-like connectivity in the remotest parts of the country with high reliability and flexibility,