Daily Current Affairs for UPSC CSE
Topics Covered
- Retail Digital Rupee
- UNDP programme to help waste seggregation workers to access govt scheme –
- CCUS –
- SARAS –3 –
- India – Canada Relationship –
- Article 25 –
- Facts for Prelims
1 . Retail Digital Rupee
Context: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on November 29 announced that the first pilot for the retail version of the digital rupee (e₹-R) would be introduced on December 1, 2022.
About the News
- The pilot would cover select locations in closed user groups (CUG) comprising participating customers and merchants.
- The e₹-R would be in the form of a digital token that represents legal tender.
- It would be issued in the same denominations as paper currency and coins are currently issued and would be distributed through banks.
- The pilot will test the robustness of the entire process of digital rupee creation, distribution and retail usage in real time.
- Different features and applications of the e₹- R token and architecture will be tested in future pilots, based on the learnings from this pilot.
- The pilot would initially cover four cities, namely Mumbai, New Delhi, Bengaluru and Bhubaneswar and later extend to Ahmedabad, Gangtok, Guwahati, Hyderabad, Indore, Kochi, Lucknow, Patna and Shimla
What will the retail digital rupee be?
- In effect, the retail e-rupee will be an electronic version of cash, and will be primarily meant for retail transactions.
- It will be potentially available for use by all — the private sector, non-financial consumers and businesses — and will be able to provide access to safe money for payment and settlement, as it will be the direct liability of the central bank.
- CBDC is the legal tender issued by a central bank in a digital form. It is the same as a fiat currency and is exchangeable one-to-one with the fiat currency. Only its form is different.
Transaction mechanism
- Users will be able to transact with e₹-R through a digital wallet offered by the participating banks and stored on mobile phones / devices.
- Transactions can be both Person-to-Person (P2P) and Person-to-Merchant (P2M).
- Payments to merchants can be made using QR codes displayed at merchant locations.
- The e₹-R would offer features of physical cash such as trust, safety and settlement finality.
- As in the case of cash, it will not earn any interest and can be converted to other forms of money, like deposits with banks.
Participating banks
- Eight banks have been identified for phase-wise participation in this pilot.
- The first phase will begin with four banks, namely State Bank of India, ICICI Bank, Yes Bank and IDFC First Bank in four cities across the country.
- Four more banks including Bank of Baroda, Union Bank of India, HDFC Bank and Kotak Mahindra Bank will join this pilot subsequently.
- The scope of the pilot may be expanded gradually to include more banks, users and locations as needed.
What is the other kind of digital rupee?
- Based on the usage and the functions performed by the digital rupee and considering the different levels of accessibility, RBI has demarcated the digital rupee into two broad categories: general purpose (retail) and wholesale.
- On November 1, the RBI launched the digital rupee for the wholesale segment to settle secondary market transactions in government securities.
- Wholesale CBDC is designed for restricted access to select financial institutions.
- It has the potential to transform the settlement systems for financial transactions undertaken by banks in the government securities (G-Sec) segment, inter-bank market and capital market more efficient and secure in terms of operational costs, use of collateral and liquidity management.
What are the advantages of the e-rupee?
- The RBI had earlier said the key motivations for exploring the issuance of CBDC in India among others include reduction in operational costs involved in physical cash management, fostering financial inclusion, bringing resilience, efficiency and innovation in the payments system.
- It will add efficiency to the settlement system and boost innovation in cross-border payments space and provide the public with uses that any private virtual currencies can provide, without the associated risks.
- The RBI has repeatedly flagged concerns over money laundering, terror financing, tax evasion, etc with private cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ether, etc. Introducing its own CBDC has been seen as a way to bridge the advantages and risks of digital currency.
2 . United Nations Development Programme to help waste segregation workers access government schemes
Context: The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) is helping the people working in the waste segregation industry in India to move into formal economy, by helping them access government welfare programmes.
Initiative
- As part of the initiative, the United Nations Under-Secretary-General Usha Rao-Monari would distribute the `Jan Dhan’ account kits to waste segregation workers during her first visit to the country, on December 1.
- The opening of the `Jan Dhan’ accounts has been facilitated through the UNDP’s plastic waste management programme.
- The waste management promotes the collection, segregation, and recycling of all plastics to move towards a circular economy for the same.
- This is done at ‘Swachhta Kendra’ or material recovery facilities.
- The plastic collected and processed so far has already crossed 1,38,000 metric tonnes, the UNDP said.
Financial inclusion of `Safai Sathis’
- The programme also ensures the well-being and financial inclusion of the `Safai Sathis’ or waste-pickers, by linking them to the social protection schemes.
- According to the UN agency, a key objective of the programme is to help move the sector from informal to formal.
- So, the UNDP has been assisting the ‘Safai Saathis’, who contribute immensely to resource management and yet occupy the lowest rung of the ladder of the circular economy.
- This is done by linking them to social protection schemes like the `Jan Dhan’ accounts, Aadhar cards, `Ayushman Bharat’, pension schemes, and scholarships for children, among others.
The need for this initiative?
- A baseline survey done by the UNDP earlier shows that the ‘Safai Sathis’ are employed mainly on the margins of the urban informal sector.
- Their low income and job security are compounded by the fact that nearly 70% come from socially- backward groups and over 60% have no formal education.
- More than 90% workers reported owning an Aadhar card but only a tiny subset have an income, caste, or occupation certificate.
- The survey says, “This thwarts any attempts at formalising their work and limits their access to government social security schemes.
- Less than 5% of those surveyed had any health insurance, indicating very high degrees of health-shock vulnerabilities”.
- Of those `Safai Sathis’ who had a bank account, only 20% were linked to the `Jan Dhan Yojana’ – the government’s flagship financial inclusion programme.
- Half of the samples reported owning and using a ration card and this proportion was even smaller in cities where migrants formed a larger share among surveyed workers.
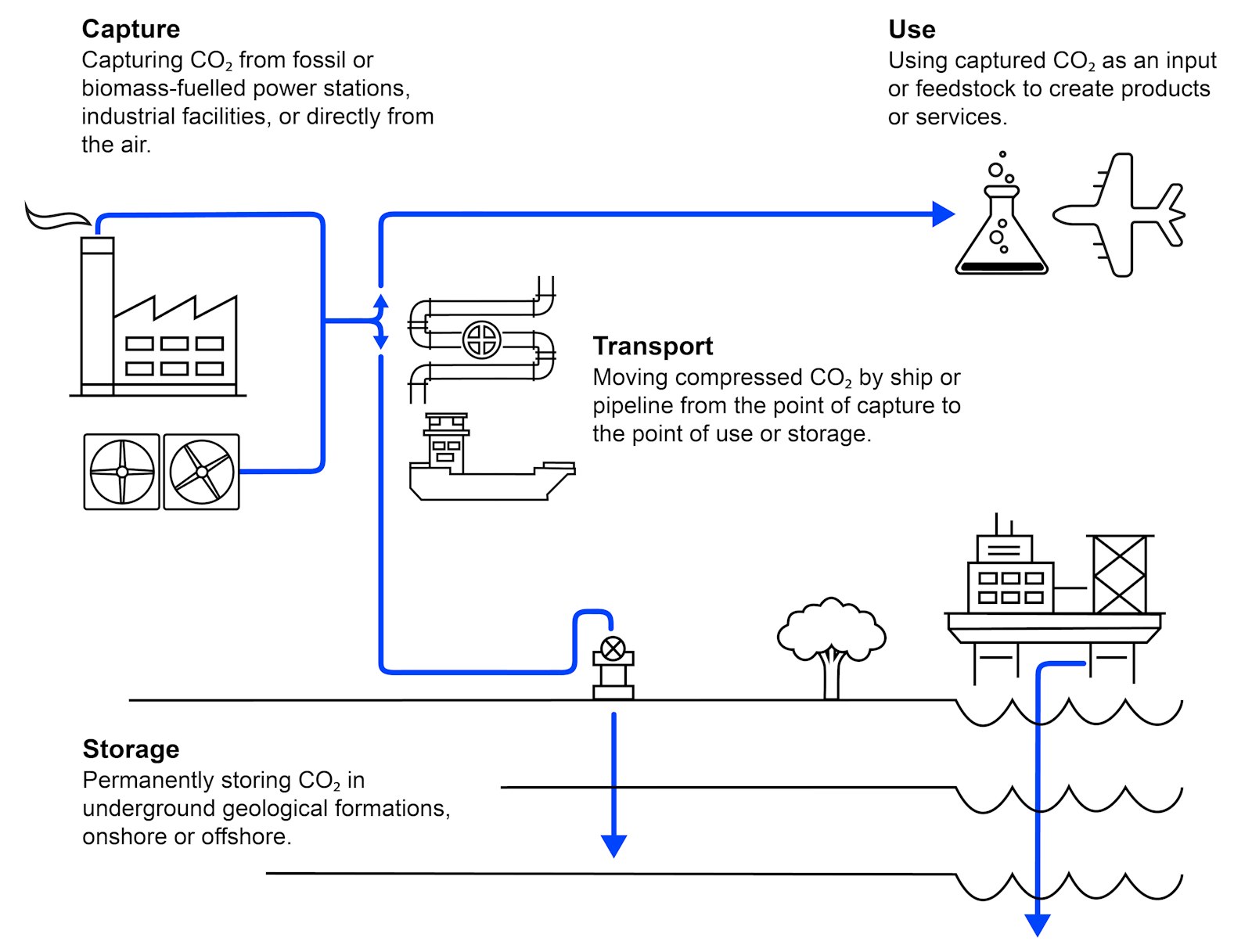
3 . Carbon Capture Utilisation and Storage (CCUS)
Context: Carbon Capture Utilisation and Storage (CCUS), the technology for decarbonising carbon dioxide (CO2) from high polluting sectors such as steel, cement, oil, gas, petrochemicals, chemicals and fertilisers, has a critical role to play for the country to halve CO2 emissions by 2050, says a report on the policy framework of the CCUS prepared by the Niti Aayog and MN Dastur & Company.
About CCUS
- Carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS) refers to a suite of technologies that can play a diverse role in meeting global energy and climate goals.
- CCUS involves the capture of CO2 from large point sources, such as power generation or industrial facilities that use either fossil fuels or biomass as fuel. The CO2 can also be captured directly from the atmosphere. If not being used on-site, the captured CO2 is compressed and transported by pipeline, ship, rail or truck to be used in a range of applications, or injected into deep geological formations (including depleted oil and gas reservoirs or saline aquifers), which can trap the CO2 for permanent storage.
- CCUS technologies also provide the foundation for carbon removal or “negative emissions” when the CO2 comes from bio-based processes or directly from the atmosphere.
What does the report say?
- The report, released by Niti Aayog Vice-Chairman Suman K. Bery, also said the CCUS technology would help in promoting the low carbon-hydrogen economy and in removal of the CO2 stock from the atmosphere.
- India’s per capita CO2 emissions were about 1.9 tonnes per annum, which was less than 40% of the global average and about one-fourth of that of China.
- India needs a sustainable solution for the decarbonisation of sectors that contribute to 70% of emission.
- CCUS has an important and critical role to play in it, especially for India to accomplish net-zero by 2070.
- CCUS could enable the production of clean products while utilising rich endowments of coal, reducing imports and thus leading to a self-reliant India economy.
- CCUS also has an important role to play in enabling sunrise sectors such as coal gasification and the nascent hydrogen economy in India.
What will CCUS do?
- Through the technology, CO2 coming from various thermal power plants or industrial plants would be captured.
- Using CCUS technology we will be able to make some valorisation of the CO2.
- There will be an impact on the economy if India is able to get value-added products such as green methanol, green ammonia can be produced from this captured CO2.
Challenges
- Key challenge would be to reduce the cost of the mechanisms to implement the technology.
Way Forward
- Key to a successful CCUS implementation in India was to enact a policy framework that supported the creation of sustainable and viable markets for CCUS projects.
- The private sector is unlikely to invest in CCUS unless there are sufficient incentives or unless it can benefit from the sale of CO2 or gain credits for emissions avoided under carbon pricing regimes.
- On the policy framework, the report suggested that in the near term, CCUS policy should be carbon credits or incentives based, to seed and promote the CCUS sector in India through tax and cash credits.
- Over time (probably beyond 2050), the policy should transition to carbon taxes, to enable reaching India’s net zero goals by 2070.
- The policy should establish early-stage financing and funding mechanisms for CCUS projects.
4 . SARAS-3 Telescope
Context: SARAS 3, a radio telescope designed and built at the Raman Research Institute (RRI) here has provided clues to the nature of the Universe’s first stars and galaxies.
About SARAS 3
- The SARAS 3 radio telescope invented and built by the astronomers at RRI is the first telescope worldwide to reach the required sensitivity.
- In 2020 the radio telescope was deployed in lakes in Northern Karnataka, on Dandiganahalli Lake and Sharavati backwaters. Living in isolated rural DRIK Viveka campus of social worker and Padma Shri award winner Anita Reddy, RRI astronomers gathered the most precise measurements to date. The focused goal during this deployment was the cross-verification of the claimed detection of the 21-cm signal by the ASU/MIT EDGES experiment.
Use of data from SARAS-
- Using data from the telescope which has been deployed over the Dandiganahalli Lake and Sharavati backwaters since 2020, astronomers and researchers have been able to determine properties of radio luminous galaxies formed just 200 million years post the Big Bang, a period known as the Cosmic Dawn.
- Researchers from the RRI and the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) in Australia, along with collaborators at the University of Cambridge and University of Tel Aviv, have used data from SARAS 3 to throw light on the energy output, luminosity, and masses of the first generation of galaxies that are bright in radio wavelengths.
- The results from the SARAS 3 telescope are the first time that radio observations of the averaged 21-centimetre line have been able to provide an insight into the properties of the earliest radio loud galaxies that are usually powered by supermassive black holes.
Research Findings
- SARAS 3 has improved the understanding of astrophysics of Cosmic Dawn by telling astronomers that less than 3% of the gaseous matter within early galaxies was converted into stars, and that the earliest galaxies that were bright in radio emission were also strong in X-rays, which heated the cosmic gas in and around the early galaxies.
5 . Article 25
Context: The right to religion does not include the right to convert other people to a particular religion, especially through fraud, deception, coercion, allurement and other means, the Home Ministry told the Supreme Court recently.
Background of the Case
- The Union government’s stand was presented in a short affidavit in response to a plea seeking direction to take stringent steps to control fraudulent religious conversion by “intimidation” and through “gifts and monetary benefits”.
- The Union government’s affidavit, filed through Deputy Secretary of Ministry of Home Affairs, asserted that the reliefs sought in the present petition would be taken up “in all seriousness” by the Union of India” and that it is “cognizant of the gravity and the seriousness of the issue raised in the present writ petition”.
- A bench of Justices M.R. Shah and C.T. Ravikumar, while hearing the matter, observed it was not against religious conversions but forced conversions, and asked the Union government to file a detailed affidavit on the issue after taking information from states.
What does Article 25 say?
- Article 25 deals with Freedom of conscience and free profession, practice and propagation of religion
- Article 25(1): Subject to public order, morality and health and to the other provisions of this Part, all persons are equally entitled to freedom of conscience and the right freely to profess, practise and propagate religion.
- Article 25(2): Nothing in this article shall affect the operation of any existing law or prevent the State from making any law—
- 25(2)(a): regulating or restricting any economic, financial, political or other secular activity which may be associated with religious practice
- 25(2)(b): providing for social welfare and reform or the throwing open of Hindu religious institutions of a public character to all classes and sections of Hindus.
What did Ministry clarify?
- The Ministry said the word ‘propagate’ in Article 25 (right to freedom of religion) does not include the right to convert.
- It is rather in the nature of a positive right to spread one’s religion by exposition of its tenets.
- The government said, “Fraudulent or induced conversion impinged upon the right to freedom of conscience of an individual apart from hampering public order and, therefore, the state is well within its power to regulate/restrict it”.
- The Centre said that the statutes enacted in the past to curb “the menace of organised, sophisticated large-scale illegal conversion” was upheld by the Supreme Court.
6 . Facts for Prelims
Binturong-
- It is an arboreal mammal also known as bearcat.
- is a viverrid native to South and Southeast Asia.
- The binturong is long and heavy, with short, stout legs.
- The Binturong is categorized as Vulnerable by the IUCN Red List because of a declining population trend that is estimated at more than 30% since the mid-1980s.
- The binturong is the only living species in the genus Arctictis.
Blyth’s tragopan-
- Blyth’s tragopan or the grey-bellied tragopan, is a pheasant that is a vulnerable species.
- The animal’s population is small and is believed to be decreasing at a rapid rate.
- Blyth’s tragopan is located in many different areas, including Bhutan through north-east India, north Myanmar to south-east Tibet, and also China.
- The total population is estimated to be about 2,500 to 9,999 birds.
- The Blyth’s tragopan is the State bird of Nagaland.
- In north-east India, deforestation is a major factor in the decreasing population of Blyth’s Tragopan as the forests are the main source of food. By removing this source, the pheasants are left with little or no food to consume. In addition, its primary habitat is in the forest.
MGNREGA – Section 27 (2)-
- Section 27 of Mahatma Gandhi NREGA states that-
- 1. The Central Government may give such directions as it may consider necessary to the State Government for the effective implementation of the provisions of this Act.
- 2. Without prejudice to the provisions of sub-section (1), the Central Government may, on receipt of any complaint regarding the issue or improper utilization of funds granted under this Act in respect of any scheme if prima facie satisfied that there is a case, cause an investigation into the complaint made, by any agency designated by it and if necessary, order stoppage of release of funds to the Scheme and institute appropriate remedial measures for its proper implementation within a reasonable period of time.
- It is expected that the instructions will ensure transparency and accountability in the effective implementation of Mahatma Gandhi NREGA across the country.
- Invoking the same provision, action was taken the West Bengal government earlier this year. The case remains unresolved.
Ransomware-
- Ransomware is a form of malware that encrypts a victim’s files. The attacker then demands a ransom from the victim to restore access to the data upon payment.
- Users are shown instructions for how to pay a fee to get the decryption key.
- The costs can range from a few hundred dollars to thousands, payable to cybercriminals in Bitcoin.
- There are a number of vectors ransomware can take to access a computer.
- One of the most common delivery systems is phishing spam — attachments that come to the victim in an email, masquerading as a file they should trust. Once they’re downloaded and opened, they can take over the victim’s computer, especially if they have built-in social engineering tools that trick users into allowing administrative access.
- Some other, more aggressive forms of ransomware, like NotPetya, exploit security holes to infect computers without needing to trick users.
- Microsoft recently released its second Cyber Signal report, which gathers intel from over 43 trillion security signals and more than 8,500 security experts.
- Highlighting the nature of Ransom-as-a-service (RaaS), the tech giant said more than 80 per cent of ransomware attacks take place because of incorrect server configurations.
Recent Military Exercises
- India-U.S. Army exercise ‘Yudh Abhyas
- ‘Ex Austra Hind’ with Australia
- Ex Agni Warrior’ with Singapore
- Ex Harimau Shakti’ with Malaysia
- Ex Garuda Shakti’ with Indonesia,
- Ex KazInd’ with Kazakhstan
New START Treaty-
- New START (Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty) is a nuclear arms reduction treaty between the United States and the Russian Federation.
- It was signed on 8 April 2010 in Prague, and, after ratification, entered into force on 5 February 2011.
- It is expected to last until 5 February 2026, having been extended in 2021.
- The treaty calls for halving the number of strategic nuclear missile launchers. A new inspection and verification regime will be established, replacing the SORT mechanism.
- It does not limit the number of operationally inactive nuclear warheads that can be stockpiled, a number in the high thousands.
- Recently, Russia has postponed nuclear weapons talks with the United States that were set to take place that week in Cairo.
- Officials from the two countries were scheduled to meet in the Egyptian capital from November 29 to December 6 to discuss resuming inspections under the New START nuclear arms reduction treaty, which had been suspended in March 2020 because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
India’s first private space vehicle launchpad-
- AgniKul Cosmos, a chennai based private space-tech start-up has set up India’s first-ever launchpad at Sriharikota.
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has supported the private player AgniKul Cosmos for setting up the launchpad.
- The Company has planned a tech demonstration mission.
- The launchpad facility, which was designed by Agnikul and built in collaboration with ISRO and IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center) has two sections to it: the AgniKul launchpad (ALP) and the AgniKul mission control center (AMCC).
- AgniKul’s first launch, a controlled and guided mission, vertical launch using a patented engine, will take place from this launch pad. The mission is a technology demonstrator mirroring the orbital launch of Agnikul, but on a scaled-down scale.
- Agnibaan is Agnikul’s highly customizable two-stage rocket, capable of carrying payloads of up to 100 kg in orbit (low-Earth orbit) at an altitude of approximately 700 km, with a plug-and-play configuration.
- Establishment of this private launchpad marks a significant step in opening the Indian space sector to private players and affirms the commitment of ISRO/DOS for facilitating the same.
Indian Ocean Commission-
- The Indian Ocean Commission is an intergovernmental organisation that links African Indian Ocean nations: Comoros, Madagascar, Mauritius, Réunion, and Seychelles.
- There are also seven observers: China, the European Union, the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie, the Sovereign Order of Malta, India, Japan and the United Nations.
- The IOC was created in 1982 in Port-Louis, Mauritius, and institutionalised in 1984 by the Victoria Agreement (Seychelles).
- In 2020, India, Japan and the United Nations become observer members.
- France is the current chair of Indian Ocean Commission (IOC) and Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS) and both countries cooperate closely in these fora.