Daily Current Affairs for UPSC CSE
- Appointment of Governors
- LIGO
- Standing Committees
- Colistin
- World Health Organization’s Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE)
- Juvenile
- Thirty Metre Telescope
1 . Appointment of Governors
Context : President Ram Nath Kovind transferred two Governors and made four new appointments across six States. New Governors will take charge of the Raj Bhavans in Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Bihar, Nagaland and Tripura.
About the News
- Madhya Pradesh Governor and former Gujarat Chief Minister Anandiben Patel has been transferred to U.P., while the former interlocutor for the Naga talks R.N. Ravi has been appointed Nagaland Governor.
- Senior Supreme Court advocate and former MP Jagdeep Dhankhar will be the new Governor of West Bengal, replacing Keshari Nath Tripathi.
- BJP veteran from Chhattisgarh Ramesh Bais has been appointed as the Governor of Tripura.
- Though appointed by the President, the Home Ministry is the nodal Ministry for the selection of Governors, who act as a bridge between the Centre and the States.
Constitutional Provisions Regarding Appointmenr of Governor
Article 155 : Appointment of Governor
- The Governor of a State shall be appointed by the President by warrant under his hand and seal.
Article 156 : Term of office of Governor.-
- The Governor shall hold office during the pleasure of the President.
- The Governor may, by writing under his hand addressed to the President, resign his office.
- Subject to the foregoing provisions of this article, a Governor shall hold office for a term of five years from the date on which he enters upon his office.
Article 157 : Qualifications for appointment as Governor
- No person shall be eligible for appointment as Governor unless he is a citizen of India and has completed the age of thirty-five years.
Article 158 : Conditions of Governor’s office
- The Governor shall not be a member of either House of Parliament or of a House of the Legislature of any State specified in the First Schedule, and if a member of either House of Parliament or of a House of the Legislature of any such State be appointed Governor, he shall be deemed to have vacated his seat in that House on the date on which he enters upon his office as Governor.
- The Governor shall not hold any other office of profit.
- The Governor shall be entitled without payment of rent to the use of his official residences and shall be also entitled to such emoluments, allowances and privileges as may be determined by Parliament by law and, until provision in that behalf is so made, such emoluments, allowances and privileges as are specified in the Second Schedule.
- The emoluments and allowances of the Governor shall not be diminished during his term of office.
Article 161 : Power of Governor to grant pardons, etc., and to suspend, remit or commute sentences in certain cases
- The Governor of a State shall have the power to grant pardons, reprieves, respites or remission of punishment or to suspend, remit or commute the sentence of any person convicted of any offence against any law relating to a matter to which the executive power of the State extends.
Other duties of Governor
- The Chief Minister shall be appointed by the Governor and the other Ministers shall be appointed by the Governor on the advice of the Chief Minster, and the Ministers shall hold office during the pleasure of the Governor.
- Before a Minister enters upon his office, the Governor shall administer to him the oaths of office and of secrecy according to the forms set out for the purpose in the Third Schedule.
2 . LIGO India
Background
- On September 14, 2015, the two LIGO detectors in the U.S., at Livingston in Louisiana, and Hanford in Washington, detected gravitational waves travelling outwards from a point 1.3 billion light years away from the earth.
- At this point, two massive black holes with masses 29 and 36 times that of the sun had merged to give off gravitational wave disturbances.
- Black holes are exotic objects that we know little about, but their immense gravitational pull which traps even the fastest object in the world, which is light, is legendary.
- When objects with such an immense gravity merge, the disturbance is felt by the very fabric of space time and travels outward from the merger, not unlike ripples on a pond surface. Thus, gravitational waves have been described as “ripples in the fabric of space time
- Following the 2015 detection, which later won the Physics Nobel (2017), the two LIGO detectors detected seven such binary black hole merger events before they were joined by the European Virgo detector in 2017. The two facilities have now detected 10 events.
- The Japanese detector, KAGRA, or Kamioka Gravitational-wave Detector, is expected to join the international network soon.
- In the meantime, in a collaboration with LIGO, a gravitational wave detector is being set up in India. The LIGO India project is expected to join the international network in a first science run in 2025.
What are the LIGO detectors?
- The acronym LIGO stands for Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory. LIGO consists of a pair of huge interferometers, each having two arms which are 4 km long.
- Remarkable precision is needed to detect a signal as faint as a gravitational wave, and the two LIGO detectors work as one unit to ensure this. Naturally, this requires weeding out noise very carefully, for when such a faint signal is being detected, even a slight human presence near the detector could derail the experiment by drowning out the signal.
- LIGO, unlike usual telescopes, does not “see” the incoming ripples in spacetime. It does not even need to, because gravitational waves are not a part of electromagnetic spectrum or light.
- They are not light waves but a different phenomenon altogether — a stretching of spacetime due to immense gravity. A single LIGO detector cannot confidently detect this disturbance on its own. At least two detectors are needed. This is because the signal is so weak that even a random noise could give out a signal that can mislead one into thinking a genuine gravitational wave has been detected. It is because two detectors have detected the faint signal in coincidence that the observer is convinced it is a genuine reading and not noise.
What is the need to have another detector in India?
- Right now, with just three detectors, there is huge uncertainty in determining where in the sky the disturbance came from. Observations from a new detector in a far-off position will help locate the source of the gravitational waves more accurately.
Possible sources of gravitational waves
- Mergers of black holes or neutron stars, rapidly rotating neutron stars, supernova explosions and the remnants of the disturbance caused by the formation of the universe, the Big Bang itself, are the strongest sources. There can be many other sources, but these are likely to be too weak to detect.
About LIGO India
- LIGO India will come up in Maharashtra, near Aundha in Hingoli district. Most of the land has been acquired, and the small balance is going through a slightly longer acquisition procedure.
- The project is formally in the construction phase, with the building design conceptualised.
- Like the LIGO detectors, the one at LIGO India will also have two arms of 4 km length. But while there are similarities there will be differences too.
- Being an ultra-high precision large-scale apparatus, LIGO India is expected to show a unique “temperament” determined by the local site characteristics.
3 . Parliamentary Committees
Background
- Eleven of the 22 Bills introduced in the ongoing session of Parliament have been passed, which makes it a highly productive session after many years.
- But these Bills have been passed without scrutiny by parliamentary standing committees, their purpose being to enable detailed consideration of a piece of legislation.
- After the formation of the 17th Lok Sabha, parliamentary standing committees have not been constituted as consultations among parties are still under way.
- Partly as a result of this, the Bills were passed without committee scrutiny. They were discussed in Parliament over durations ranging between two and five hours.
Need of parliamentary committees
- Committees are an instrument of Parliament for its own effective functioning.
- Given the volume of legislative business, discussing all Bills under the consideration of Parliament in detail on the floor of the House is impossible.
- Committees are platforms for detailed discussion on a proposed law. Committee meetings are ‘closed door’ and members are not bound by party whips, which allows them the latitude for a more meaningful exchange of views as against discussions in full and open Houses where grandstanding and party positions invariably take precedence.
- Executive accountability to the legislature is enforced through questions in Parliament also, which are answered by ministers. However, department standing committees go one step further and hear from senior officials of the government in a closed setting, allowing for more detailed discussions. This mechanism also enables parliamentarians to understand the executive processes closely.
Origins
- As is the case with several other practices of Indian parliamentary democracy, the institution of Parliamentary Committees also has its origins in the British Parliament.
- The first Parliamentary Committee was constituted in 1571 in Britain.
- The Public Accounts Committee was established in 1861.
- In India, the first Public Accounts Committee was constituted in April 1950.
- The practice of regularly referring bills to committees began in 1989 after government departments started forming their own standing committees. Prior to that, select committees or joint committees of the houses were only set up to scrutinise in detail some very important bills, but this was few and far between.”
Constitutional Provisions
- Parliamentary committees draw their authority from Article 105 (on privileges of Parliament members) and Article 118 (on Parliament’s authority to make rules for regulating its procedure and conduct of business).
- Committee reports are usually exhaustive and provide authentic information on matters related to governance.
- Bills that are referred to committees are returned to the House with significant value addition. Parliament is not bound by the recommendations of committees.
Types of committees
- Most committees are ‘standing’ as their existence is uninterrupted and usually reconstituted on an annual basis; some are ‘select’ committees formed for a specific purpose, for instance, to deliberate on a particular bill.
- Once the Bill is disposed of, that select committee ceases to exist. Some standing committees are departmentally related, an example being the Standing Committee on Human Resource Development.
- A Bill related to education could either be considered by the department standing committee or a select committee that will be specifically set up.
- The chair uses her discretion to refer a matter to a parliamentary committee but this is usually done in consultation with leaders of parties in the House.
- Financial control is a critical tool for Parliament’s authority over the executive; hence finance committees are considered to be particularly powerful. The three financial committees are the Public Accounts Committee, the Estimates Committee and the Committee on Public Undertakings.
4 . Colistin
Context : The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has issued an order prohibiting the manufacture, sale and distribution of colistin and its formulations for food-producing animals, poultry, aqua farming and animal feed supplements.
About Colistin
- According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), Colistin is a “reserve” antibiotic, which means it is supposed to be considered a “last-resort” option in treatment and used only in the most severe circumstances, when all other alternatives have failed.
Issue
- Colistin has been “highly misused” in India’s livestock industry to prevent diseases and as promote growth of such animals
- One of the reasons for anti microbial resistance in India is due to unwanted use of Colistin in the poultry industry,
About the recent govt order
- The order directed manufacturers of colistin and its formulations (since it is also used to treat humans) to affix a label on the container reading thus: Not to be used in food producing animals, poultry, aqua farming and animal feed supplements: on the package, insert and promotional literature.
- Cutting the use of colistin in the food industry, particularly as growth supplements used in animals, poultry, aqua farms, and limiting it to therapeutic usage only would likely reduce the antimicrobial resistance within the country.
5 . World Health Organization’s Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE)
Context : The phase-3 clinical trial involving thousands of volunteers tested the efficacy of Merck’s vaccine (VSV-EBOV) to protect vaccinated individuals from getting infected with Ebola virus. Preliminary data from vaccination in Congo suggest the vaccine has 97.5% efficacy in preventing Ebola. World Health Organization’s Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) had in March 2017, recommended that in the absence of a licensed vaccine for Ebola, the investigational vaccine could be used during an outbreak caused by the Zaire strain of the virus.
About SAGE
- The Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) on Immunization was established by the Director-General of the World Health Organization in 1999 to provide guidance on the work of WHO.
- SAGE is the principal advisory group to WHO for vaccines and immunization.
- It is charged with advising WHO on overall global policies and strategies, ranging from vaccines and technology, research and development, to delivery of immunization and its linkages with other health interventions.
- SAGE is concerned not just with childhood vaccines and immunization, but all vaccine-preventable diseases.
6 . Juvenile
When is a child tried as an adult?
- The Juvenile Justice Act of 2000 was amended in 2015 with a provision allowing for Children in Conflict with Law (CCL) to be tried as adults under certain circumstances. The Act defines a child as someone who is under age 18. For a CCL, age on the date of the offence is the basis for determining whether he or she was a child or an adult.
- The amended Act distinguishes children in the age group 16-18 as a category which can be tried as adults if they are alleged to have committed a heinous offence — one that attracts a minimum punishment of seven years. The Act does not, however, make it mandatory for all children in this age group to be tried as adults.
7 . Thirty Metre Telescope
Context : Hawaii saw protests against plans to start construction of a giant telescope atop Mauna Kea, the US state’s highest mountain at 14,000 feet. Already the site of a number of observatories and 13 large telescopes, Mauna Kea is considered sacred by native Hawaiians who believe that such constructions defile the mountain. After a Supreme Court order recently cleared construction of the newest one, called the “Thirty Metre Telescope”, locals blocked access to the roads last week, leading to several arrests.
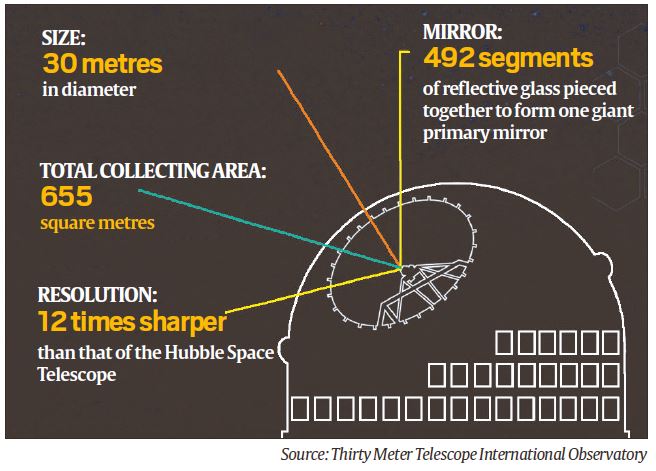
About Thirty Metre Telescope
- The telescope is being built by an international collaboration of government organisations and educational institutions, at a cost of $1.4 billion. “Thirty Metre” refers to the the 30-metre diameter of the mirror, with 492 segments of glass pieced together, which makes it three times as wide as the world’s largest existing visible-light telescope.
- The larger the mirror, the more light a telescope can collect, which means, in turn, that it can “see” farther, fainter objects.
- Telescope would be more than 200 times more sensitive than current telescopes, and would be able to resolve objects 12 times better than the Hubble Space Telescope.
- One of its key uses will be the study of exoplanets, many of which have been detected in the last few years, and whether their atmospheres contain water vapour or methane — the signatures of possible life. The study of black holes is another objective. While these have been observed in detail within the Milky Way, the next galaxy is 100 times farther away; the Thirty Metre Telescope will help bring them closer.
Map Based Questions
- Canary Island
- Mauna Kea