Daily Current Affairs for UPSC CSE
Topics covered
- National sample survey by ICRIER and LIRNE Asia
- Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)
- National Achievement Survey test
- Facts for Prelims
1. National sample survey by ICRIER and LIRNEAsia
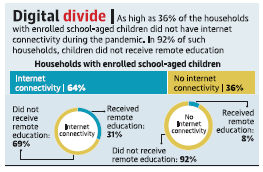
Context: Only 20% of schoolage children in India had access to remote education during
the pandemic, of whom only half participated in live online lessons, according to a new national sample survey by ICRIER and LIRNEAsia, a think tank focused on digital policy.
About the Survey
- The face to face survey, conducted between March and August this year, covered a nationally representative sample of 7,000 households.
- Only Kerala was excluded, due to high COVID19 cases.
Key findings
- Only 20% of school age children in India had access to remote education during the pandemic, of whom only half participated in live online lessons.
- 38% of households said at least one child had dropped out of school due to COVID19.
- The survey found that although digital connectivity shot up 40% during the pandemic, low access to devices, poor signal and high costs prevented most children from reaping the benefits.
- Among children aged 5-18, it found that 80% of those who were enrolled in schools prior to the pandemic did not receive any educational services at all during school closure.
- The situation was significantly worse among those from lower socioeconomic classes, where the head of the household had lower education levels, and among rural households.
- Among the 20% who received education, only 55% had access to live online classes, while 68% had access to recorded audio or video lessons.
- Three-fourths of the students had work sent to them over a smartphone, usually via WhatsApp, and 61% via text messages.
- Almost 70% had contact with their teachers via phone calls.
2. Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)
Context : States in the National Capital Region were on Friday directed to be ready to implement
actions under the ‘emergency’ category of the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) to control air
pollution. A subcommittee under the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) in NCR and adjoining areas, which gave the direction on GRAP, also advised Government and private offices and other establishments to reduce vehicle usage by 30%.
About GRAP
- GRAP is a set of emergency measures to be taken to reduce the air pollution depending on the level of pollution.
- GRAP is a plan that institutionalised measures to be taken when air quality deteriorates.
- It was approved by the Supreme Court in 2016, the plan was formulated after several meetings that the Environment Pollution (Prevention and Control) Authority (EPCA) held with state government representatives and experts.
- GRAP works only as an emergency measure. If air quality reaches the severe+ stage, GRAP talks about shutting down schools and implementing the odd-even road-space rationing scheme.
- GRAP was notified in 2017 by the Centre and draws its authority from this notification
- Plan has been prepared for implementation under different Air Quality Index (AQI) categories namely, Moderate & Poor, Very Poor, and Severe as per National Air Quality Index. A new category of “Severe+ or Emergency” has been added
Implementation under different Air Quality Index (AQI)
- Severe+ or Emergency (PM 2.5 over 300 µg/cubic metre or PM10 over 500 µg/cu. m. for 48+ hours)
- Stop entry of trucks into Delhi (except essential commodities)
- Stop construction work
- Introduce odd/even scheme for private vehicles and minimise exemptions
- Task Force to decide any additional steps including shutting of schools
- Severe (PM 2.5 over 250 µg/cu. m. or PM10 over 430 µg/cu. m.)
- Close brick kilns, hot mix plants, stone crushers
- Maximise power generation from natural gas to reduce generation from coal
- Encourage public transport, with differential rates
- More frequent mechanised cleaning of road and sprinkling of water
- Very Poor (PM2.5 121-250 µg/cu. m. or PM10 351-430 µg/cu. m.)
- Stop use of diesel generator sets
- Enhance parking fee by 3-4 times
- Increase bus and Metro services
- Apartment owners to discourage burning fires in winter by providing electric heaters during winter
- Advisories to people with respiratory and cardiac conditions to restrict outdoor movement
- Moderate to poor (PM2.5 61-120 µg/cu. m. or PM10 101-350 µg/cu. m.)
- Heavy fines for garbage burning
- Close/enforce pollution control regulations in brick kilns and industries
- Mechanised sweeping on roads with heavy traffic and water sprinkling
- Strictly enforce ban on firecrackers
3. National Achievement Survey
Context: The first National Achievement Survey (NAS) in four years was conducted on Friday,
in a bid to assess the competencies of children in Class 3, 5 and 8. This will “help to assess the learning interruptions and new learnings during the COVID pandemic and help to take remedial
measures,” said the Education Ministry
About NAS
- National Achievement Survey (NAS) is a nationally representative large-scale survey of students’ learning undertaken by the Ministry of Education, Government of India.
- NAS gives a system level reflection on effectiveness of school education.
- Findings help compare the performance across spectrum and across population in order to find the desirable direction for improvements.
- The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) has developed the Assessment Framework for gauging the competencies attained by the students vis-a-vis learning outcomes.
- The Survey goes beyond the scorecard and includes the background variables to correlate student’s performance in different learning outcomes vis-a-vis contextual variables.
How is it Conducted?
- This national level survey would be conducted by the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) as Assessment Administrator for Grade 3, 5, 8 and 10 students of State Govt. schools, Govt. Aided schools, Private Unaided recognized schools and Central Government schools.
- The Survey will be conducted in a monitored environment in the sampled schools.
- Sampling Design for NAS 2021 intends to support the predefined and agreed objectives of the national assessment, NAS 2021 intends to provide information of what India’s students know and can do in key grades and subjects at national, state, district and school type.
- Selection of sampled schools is based on UDISE+2019-20 data. Therefore, the States, Districts used for drawing of the samples for NAS 2021 is exactly as per the UDISE+2019-20.
How does it help improve education system?
- NAS findings would help diagnose learning gaps of students and determine interventions required in education policies, teaching practices and learning.
- Through its diagnostic report cards, NAS findings help in capacity building for teachers, officials involved in the delivery of education.
- NAS 2021 would be a rich repository of evidences and data points furthering the scope of research and development.
- With this in view, NAS-2021 Portal has been developed by NIC as a dynamic platform in consultation with the NCERT, CBSE, UNICEF, DDG (Stats) and NITI Aayog under the overall guidance of Ministry of Education, Government of India.
- This portal would be a sustainable educational management information system both for helping in smooth conduct of NAS-2021 as well as for future decision-making based on data analytics. The portal provides role-based functionality and dashboard for managing the resources (various functionaries involved in the conduct & administration of NAS), activity and event monitoring, capacity building, reporting & documentation, post NAS analytical report in the customized formats.
4. Facts for Prelims
World Food Programme
- The World Food Programme is the food-assistance branch of the United Nations.
- It is the world’s largest humanitarian organization, the largest one focused on hunger and food security, and the largest provider of school meals.
- It was established in 1961.
- It launched its first development programme in 1963 for Nubians in Sudan. In the same year, the WFP’s first school meals project – in Togo – was approved. Two years later, WFP became a full-fledged UN programme.
- The WFP is headquartered in Rome, Italy.
- It is governed by an Executive Board, which consists of 36 member states.
- It is headed by an Executive Director, who is appointed jointly by the UN Secretary-General and the Director-General of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The Executive Director is appointed for fixed five-year terms.
Secretary General of Rajya Sabha
- The SG is the parliamentary adviser to the RS chairman and through him to the House.
- The SG is also the administrative head of the RS Secretariat and overall in-charge of all administrative and executive functions on behalf of, and in the name of, the Chairman
Norovirus
- Norovirus is an animal-borne disease transmitted through contaminated water and food
- Norovirus is a very contagious virus that causes vomiting and diarrhea.
- Norovirus is sometimes referred to as the winter vomiting bug
- You can get norovirus from:
- Having direct contact with an infected person
- Consuming contaminated food or water
- Touching contaminated surfaces and then putting your unwashed hands in your mouth.
- The most common symptoms are:
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Stomach pain
- Kerala has been put on alert after at least 13 cases of norovirus have been recorded in Wayanad district.
Landraces
- Landraces refer to naturally occurring variants of commonly cultivated crops.
- These are as opposed to commercially grown crops, which are developed by selective breeding (hybrids) or through genetic engineering to express a certain trait over others.
Index of Industrial Production (IIP)
- The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) is a composite indicator that measures the short-term changes in the volume of production of a basket of industrial products during a given period with respect to that in a chosen base period.
- In India, the first official attempt to compute the Index of Industrial Production (IIP) was made much earlier than the first recommendation on the subject came at the international level.
- With the inception of the Central Statistical Organization (now known as National Statistics Office (NSO)) in 1951, the responsibility for compilation and publication of IIP was vested with it.
- IIP is a composite indicator that measures the growth rate of industry groups classified under,
- Broad sectors, namely, Mining, Manufacturing and Electricity
- Use-based sectors, namely Basic Goods, Capital Goods and Intermediate Goods.
- The base year was changed to 2011-12 from 2004-05 in the year 2017.
- The data is used by Ministry of Finance, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), private firms and analysts, among others for analytical purposes.
- The data is also used to compile the Gross Value Added (GVA) of the manufacturing sector in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) on a quarterly basis.
IIP Index Components:
- Electricity, crude oil, coal, cement, steel, refinery products, natural gas, and fertilisers are the eight core industries that comprise about 40 percent of the weight of items included in the Index of Industrial Production.
- Mining, manufacturing, and electricity are the three broad sectors in which IIP constituents fall.