Daily Current Affairs for UPSC CSE
Topics Covered
- Defence Ministry to impose import embargo on 101 items
- New financing scheme under Agriculture Infrastructure Fund
- Submarine Optical Fiber
- Asymptomatic people too carry high viral loads
- Plasmodium vivax
- Sun’s coronal magnetic field
- Confucius Institutes
- Facts for Prelims
1 . Defence Ministry to impose import embargo on 101 items
Context: The Ministry of Defence has recently announced a list of 101 items that the Defence Ministry will stop importing.
Background
- For years India has been among the top three defence importers in the world
- As per Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, India has been the second largest importer between 2014 and 2019 with US$ 16.75 billion worth of imports during this period.
About the news
- The move essentially means that the Armed Forces—Army, Navy and Air Force—will only procure all of these 101 items from domestic manufacturers ( private sector players or defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs)).
Benefits
- The domestic manufacturers are given opportunity to manufacture the items in the negative list by using their own design and development capabilities.
- They can also adopt the technologies of Defence Research and Development Organisation to meet the requirements of the Armed Forces.
- The import embargo on 101 items will give a boost to indigenisation of defence production.
- The government hopes that defence manufacturing sector can play a leading role in boosting the economy and become an exporter as well.
What does it include?
- The negative list has a range of items from simpler items to advanced technologies.
- The list includes water jet fast attack craft to survey vessels, pollution control vessels, light transport aircraft, GSAT-6 terminals, radars, unmanned aerial vehicles, to certain rifles, artillery guns, bullet proof jackets, missile destroyers, etc.
When will it come into effect?
- The embargo on imports is planned to be progressively implemented between 2020 to 2024
- Of the 101 items mentioned 69 have an indicative embargo of December 2020. Another 11 have an indicative embargo of end of next year. The 12 are likely to be embargoed by December 2023, another 8 by end of 2024, and one item Long Range – Land Attack Cruise Missile will not be allowed to be imported after December 2025.
Significance
- This will boost indigenisation of defence production.
- This is in line with the government’s target to reach a turnover of $25 billion through indigenously manufactured defence products and also to export products worth $5 billion.
- The move to not include a foreign company in the tendering process in any government contract over ₹200 crore will help Indian defence manufacturers
- This will be a step towards Atma nirbhar Bharat.
2 . New financing scheme under Agriculture Infrastructure Fund
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi has launched a new financing scheme under the ₹1 lakh crore Agriculture Infrastructure Fund.
About the scheme
- The first ₹1,000 crore was sanctioned to over 2,280 farmer societies under the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund.
- The scheme will support farmers, PACS [primary agricultural credit societies], FPOs [farmer producer organisations], agri-entrepreneurs, etc. in building community farming assets and post-harvest agriculture infrastructure.
- These assets will enable farmers to get greater value for their produce as they will be able to store and sell at higher prices, reduce wastage, and increase processing and value addition
Significance
- This will help in setting up storage and processing facilities, which will help farmers get higher prices for their crops
- The scheme would give farmers and the agriculture sector a boost and “increase India’s ability to compete on the global stage”.
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund
- It is a new pan India Central Sector Scheme
- The scheme shall provide a medium – long term debt financing facility for investment in viable projects for post-harvest management Infrastructure and community farming assets through interest subvention and financial support.
- The duration of the Scheme shall be from FY2020 to FY2029 (10 years).
- Intended Beneficiaries: Under the scheme, Rs. One Lakh Crore will be provided by banks and financial institutions as loans to Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS), Marketing Cooperative Societies, Farmer Producers Organizations (FPOs), Self Help Group (SHG), Farmers, Joint Liability Groups (JLG), Multipurpose Cooperative Societies, Agri-entrepreneurs, Startups, Aggregation Infrastructure Providers and Central/State agency or Local Body sponsored Public Private Partnership Project.
Benefits
- All loans under this financing facility will have interest subvention of 3% per annum up to a limit of Rs. 2 crore. This subvention will be available for a maximum period of seven years.
- Further, credit guarantee coverage will be available for eligible borrowers from this financing facility under Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE) scheme for a loan up to Rs. 2 crore. The fee for this coverage will be paid by the Government.
- In case of FPOs the credit guarantee may be availed from the facility created under FPO promotion scheme of Department of Agriculture, Cooperation & Farmers Welfare (DACFW).
- Moratorium for repayment under this financing facility may vary subject to minimum of 6 months and maximum of 2 years.
3 . Andaman and Nicobar will be a maritime hub
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi has declared that the Andaman and Nicobar islands region will be developed as a “maritime and startup hub”.
About the news
- 12 islands of the archipelago have been selected for high-impact projects with an emphasis on boosting trade of sea-based, organic and coconut-based products of the region.
Government initiatives
- Transhipment Hub – A transhipment hub has been proposed in the Andamans. The transshipment port is proposed to be built at Great Nicobar at an estimated expenditure of about Rs 10,000 crore. It will provide Indian shippers an alternative to the Colombo (Sri Lanka), Singapore and Port Klang (Malaysia) transshipment ports.
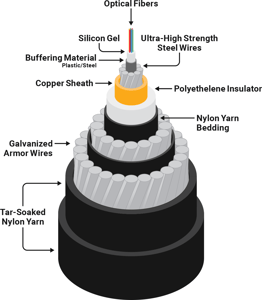
- Submarine optical fibre : A submarine optical fibre cable between Chennai and islands will be inaugurated. Undersea cable will link the Andaman and Nicobar Islands with Chennai. The work of laying undersea cable has been executed by BSNL in a record time of less than 24 months. The cable was laid at a cost of Rs 1,224 crore and it will provide “better and cheaper connectivity”. An internet speed of 400 gigabytes (Gb) per second will be provided at Port Blair and for other islands, it will be 200 Gb per second.
- Physical connectivity through road, air, and water is also being strengthened. Two big bridges and widening of National Highway No.4 is being undertaken to improve road connectivity between North and Middle Andaman. The Port Blair Airport is being enhanced to handle a capacity of 1,200 passengers. The airports are ready for operations in Diglipur, Car Nicobar, and Campbell-Bay. Seaplane services will also start once water aerodrome infrastructure including passenger terminal and floating jetty is ready at Swaraj Dweep, Shaheed Dweep, and Long Island. Four ships which are being built at Kochi Shipyard shall be delivered soon to improve the water connectivity between the islands and the mainland.
Submarine Optical Fiber
- Undersea cable will link the Andaman and Nicobar Islands with Chennai
How do cables work?
- Modern submarine cables use fiber-optic technology. Lasers on one end fire at extremely rapid rates down thin glass fibers to receptors at the other end of the cable. These glass fibers are wrapped in layers of plastic (and sometimes steel wire) for protection.

How thick are undersea cables?
- For most of its journey across the ocean, a cable is typically as wide as a garden hose. The filaments that carry light signals are extremely thin — roughly the diameter of a human hair.
- These fibers are sheathed in a few layers of insulation and protection. Cables laid nearer to shore use extra layers of armoring for enhanced protection.
Do the cables actually lie on the bottom of the ocean floor?
- Yes, cables go all the way down. Nearer to the shore cables are buried under the seabed for protection, which explains why you don’t see cables when you go the beach, but in the deep sea they are laid directly on the ocean floor.
- Of course, considerable care is taken to ensure cables follow the safest path to avoid fault zones, fishing zones, anchoring areas, and other dangers. To reduce inadvertent damage, the undersea cable industry also spends a lot of time educating other marine industries on the location of cables.
Benefits
- It will help boost tourism as it will provide better mobile and internet connectivity on the Islands
- It will boost 4G mobile services and digital services like tele-education, telehealth, e-governance services and tourism on the Islands.
- Small enterprises will benefit from the opportunities in e-commerce.
- Educational institutions will utilise the enhanced availability of bandwidth for e-learning and knowledge-sharing.
- Business Process Outsourcing services and other medium and large enterprises will also reap the benefits of better connectivity.
- It will connect other islands namely Swaraj Dweep (Havlock), Long Island, Rangat, Little Andaman, Kamorta, Car Nicobar, and Greater Nicobar.
- The dedicated container transshipment terminal
- It will offer proximity to the busy east-west international shipping route that can facilitate shorter transits and greater economies of scale, and deep natural water depths that can accommodate the latest generation of mega-ships.
- It will help the group of islands become an important centre of blue economy and a maritime and startup hub
4 . Asymptomatic people too carry high viral loads
Context: A body of evidence now suggests that people without symptoms can and do readily spread coronavirus, and people are most infectious just a couple of days before symptoms show up. This is typically the presymptomatic phase when infected people don’t exhibit symptoms but do shed substantial amounts of virus.
Details of the Study
- A retrospective study of 303 symptomatic and asymptomatic patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 during March 6-26 has found definite evidence that people who do not exhibit symptoms carry the same amount of virus as those who are symptomatic.
- Of the 303 patients studied, 110 (36.3%) were asymptomatic at the time of isolation. The team, led by Dr Eunjung Lee from the Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Bucheon, South Korea, found that only 21 of 110 asymptomatic patients subsequently developed symptoms.
- This study thus provided the much-needed evidence that many people with coronavirus infection can remain asymptomatic for a “prolonged period”.
- While this study found that 29% of asymptomatic patients never developed symptoms at all
- While the incidence of asymptomatic patients carrying high viral load raises the possibility of such people spreading the virus to others, the study did not determine this, as it was not designed for the said purpose. Both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients were isolated, thus providing no opportunity to study the chain of transmission. Also, live virus was not cultured (grown) in labs to confirm the infectious nature of the virus. Hence, they note that “detection of viral RNA does not equate infectious virus being present and transmissible”.
- While several studies too have found a large percentage of asymptomatic cases, such studies have a limitation. Unlike the current study, earlier ones had considered presymptomatic patients as asymptomatic without observing the clinical course of asymptomatic cases.
Challenges with asymptomatic infection
- The challenge with asymptomatic infection is the heightened risk of such people travelling freely and mingling with others thus spreading the virus to them.
- This will be a challenge in containing the spread of novel coronavirus
Significance of the study
- The study has underscored the importance of wearing masks and maintaining physical distancing to reduce the chances of getting infected.
- It has shown that universal masking reduces the amount virus inhaled thus increasing the chances of coming down with only mild disease even when infected.
5 . Plasmodium vivax
Context : The parasite Plasmodium vivax, responsible for 7.5 million malaria cases worldwide, remains understudied. An international team has developed a system to breed parasites Plasmodium vivax in the lab and then infect cultured human liver cells with it. This can help establish a robust liver stage assay in P. vivax-endemic regions such as India.
About Plasmodium vivax
- Malaria is a significant global health problem with a substantial disease burden worldwide. In 2017 there were approximately 219 million cases of malaria responsible for about 435000 deaths, the majority on the African continent (WHO World Malaria Report 2018).
- Malaria results from infection with single-celled parasites belonging to the Plasmodium genus. Five species of Plasmodium are known to cause disease in humans: P. falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, P. malariae, and P. knowlesi.
- Globally, Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax account for the majority of cases of malaria.
- While Plasmodium falciparum is responsible for more deaths, Plasmodium vivax is the most widespread of all of the malaria species, can cause severe, even fatal infections and results in significant global morbidity and mortality.
About the New Method
- An improved method for breeding Anopheles stephensi mosquitoes in the lab was developed.
- The females were fed with blood collected from Indian patients with the P. vivax infection.
- Two weeks later, the mature sporozoites were taken from the mosquitoes’ salivary glands, added to cultured liver cells (multiple human hepatocyte platforms) and studied.
- This approach can be used to further study the liver stage.
How do mosquitoes inject the parasite?
- Mosquitoes inject the sporozoite (spore-like) stage of the parasite into the skin when they bite, and the sporozoites travel to the liver.
- Some 50 parasites enter our liver and each infect one liver cell or hepatocyte and multiply enormously to 10,000 or more.
- These can then move out and infect blood cells.
- Not much is known about its dormant stage in the liver. The study can help establish a robust liver stage assay in P. vivax-endemic regions such as India.
- As the number is very low in the liver, our immune system barely notices it. This was believed to be a silent stage.
- The parasite can remain in the liver in a dormant stage and relapse later. So there is an urgent need to find drugs for P. vivax which will kill both the blood and liver stages
Drug Resistant Malaria Parasites
- Certain malaria-endemic countries have abandoned chloroquine for P. vivax treatment. Fortunately chloroquine is still effective in India.
- But the currently used anti-relapse drug, Primaquine, has many undesirable side-effects, especially in patients with a genetic defect called G6PD deficiency. Moreover, it takes 14 days to administer this drug for radical cure
- Hence there is an urgent need for development of a new class of drugs. The researchers add that this assay could also be used to test if a specific anti-malarial drug would work for an individual, thus paving the way for individualised treatment for patients.
6 . Sun’s coronal magnetic field
Context : An international team of solar physicists led by those from Peking University, China, and National Center for Atmospheric Research of the U.S have measured the global magnetic field of the sun’s corona, or outer atmosphere, for the very first time. This research has been published in the journal Science.
Details of the findings
- The Sun is our closest star and it is being studied for a long time.Yet, it has many associated puzzles that are unexplained. There are two main puzzles about the Sun which this advancement will help address.
- Coronal heating problem : What causes the atmosphere of the Sun (corona) to heat up again, though the surface (photosphere) is cooler than the interior?
- The core of the Sun is at a temperature of about 15 million degrees and its outer layer, the photosphere is a mere 5700 degrees hot.
- However, its corona or outer atmosphere, which stretches up to several million kilometres beyond its surface, is much, much hotter than the surface. It is at a temperature of one million degrees or more.
- Solar eruptions :
- The other set of questions concerns the mechanisms of eruptions of the Sun, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections.
- These are driven by magnetic reconnections happening in the sun’s corona.
What is Magnetic reconnection?
- Magnetic reconnection is a process where oppositely polarity magnetic field lines connect and some of the magnetic energy is converted to heat energy and also kinetic energy which leads to the generation of heating, solar flares, solar jets, etc.
What technique was used to measure coronal magnetic field?
- The team used a technique known as coronal seismology or magnetoseismology to measure the coronal magnetic field which has been known for a few decades.
- This method requires the measurement of the properties of magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) waves and the density of the corona simultaneously.
- In the past, these techniques were occasionally used in small regions of the corona, or some coronal loops due to limitations of our instruments/and proper data analysis techniques,”
- The team used the improved measurements of the Coronal Multi-channel Polarimeter (CoMP) and advanced data analysis to measure the coronal magnetic field. CoMP is an instrument operated by High Altitude Observatory, of the U.S. It is located at Mauna Loa Solar Observatory, near the summit of that volcano on the big island of Hawaii.
Why is it important to measure coronal magnetic field?
- It is very important to measure the corneal magnetic fields regularly since the solar corona is highly dynamic and varies within seconds to a minute time scale.
Aditya-L1 satellite
- While ground-based measurements pose challenges, India’s first solar mission, Aditya-L1 satellite will aim to measure the solar coronal magnetic fields regularly. This will help understand the spectacular solar eruptions and predictions of space weather and many more things.
Properties of Waves & Magnetohydrodynamic
- The properties of waves depend on the medium in which they travel. By measuring certain wave properties and doing a reverse calculation, some of the properties of the medium through which they have travelled may be, in principle, obtained.
- Waves can be longitudinal waves (for example, sound waves) or transverse waves (for example, ripples on a lake surface).
- The waves that propagate through a magnetic plasma are called magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) waves.
- There are different types of MHD waves, and one of these is the transverse MHD wave. From the theoretical calculation, it can be shown that the properties of the transverse MHD wave are directly related to the strength of magnetic fields and the density of the corona.
- Importance – Once we measure the wave properties and the density of the corona, then by using the mathematical formula (derived from MHD theory), we can compute the magnetic fields in the corona. And the CoMP instrument is uniquely designed to measure these quantities and hence the magnetic fields
7 . Confucius Institutes
Context : On July 29, India’s Ministry of Education (previously the Ministry of Human Resource Development) sent a letter to several institutions seeking information about the activities of their Confucius Institutes (CIs) and Chinese language training centres.
About the news
- This was a part of a review of work being done by higher education institutions in partnership with foreign entities.
- The move has brought the spotlight to China’s CI programme, a key pillar of Beijing’s global soft power effort, and raised questions about the future of India-China cooperation in the education space.
What are Confucius Institutes (CI)?
- Starting with a CI in Seoul in 2004, China’s National Office for Teaching Chinese as a Foreign Language (NOCFL), known as Hanban, has established 550 CIs and 1,172 Confucius Classrooms (CCs) housed in foreign institutions, in 162 countries.
- The Hanban is under the Ministry of Education.
- As the Hanban explains on its website, following the experience of the British Council, Alliance Française and Germany’s Goethe-Institut, China began “establishing non-profit public institutions which aim to promote Chinese language and culture in foreign countries”. These were named CIs.
What is the presence of CIs in India?
- India is reviewing the presence of CIs in seven universities, in addition to 54 MoUs on inter-school cooperation involving China, which is not connected to the CI programme.
- The Hanban website lists three CIs in India (University of Mumbai, Vellore Institute of Technology and Lovely Professional University) and three CCs (School of Chinese Language Kolkata, Bharathiar University, and K.R. Mangalam University) but in some of these cases, it is understood that plans did not materialise.
How have CIs been viewed around the world?
- The CI arrangement has generated debate in the West, where some universities have closed the institutes amid concern over the influence of the Chinese government on host institutions, which receive funding for running the CIs.
- Closures of some CIs have been reported in the United States, Denmark, the Netherlands, Belgium, France and Sweden.
- The Hanban has been renamed as a Center for Language Education and Cooperation, with suggestions that the Confucius Institute brand may even be dropped.
- While the closures in the West have made news, these cases still represent a minority.
- Most of the 550 CIs and more than 1,000 CCs around the world are still active, with a presence spanning Africa, Central Asia, Latin America, and across Asia, including in India’s neighbourhood in Pakistan (seven), Nepal (four), Sri Lanka (four) and Bangladesh (three), according to Hanban’s figures.
What does the CI review mean for India-China relations?
- CIs and CCs had already been in India for more than 10 years
- Even prior to the June 15 India-China border clash, Indian authorities had viewed the CI arrangement somewhat warily and as treading a fine line with regard to its rules for how foreign educational institutions can operate in India
- Along with the new move to review CIs, Mandarin has been dropped from the list of foreign languages that can be taught in schools in the new National Education Policy.
8 . Facts for Prelims
WHO solidarity Trial
- Solidarity is an international clinical trial to help find an effective treatment for COVID-19, launched by the World Health Organization and partners.
- The Solidarity Trial compares options against standard of care, to assess their relative effectiveness against COVID-19. By enrolling patients in multiple countries, the Solidarity Trial aims to rapidly discover whether any of the drugs slow disease progression or improve survival. Other drugs can be added based on emerging evidence.
Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanisation (SMAM)
- The Centre has released ₹553 crore to States under a scheme to promote mechanisation in the agriculture sector.
- The Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanisation (SMAM) was introduced in April 2014 with an aim to have inclusive growth of farm mechanisation to boost productivity.